Page 390 - Pipeline Risk Management Manual Ideas, Techniques, and Resources
P. 390
Other considerations 1365
If the pipe is considered to be unrestrained longitudinally, the In general, flexible pipes are less susceptible to damage from
longitudinal stress is numerically equal to about one-half of the these causes because the pipe can deflect and adjust to chang-
hoop stress. In most cases, the actual stress situation is some- ing lateral supports. In the case of either flexible or rigid pipes,
where between the totally restrained and totally unrestrained design considerations must be given.
conditions. A rule of thumb for buried steel pipelines shows Beam formulas are usually used to calculate bending stresses.
that the longitudinal stress generated by internal pressure can Assumptions are made as to the end conditions because this is a
be approximated by [90]: critical aspect of the beam calculations. Whether or not the pipe
is free to move in the longitudinal direction determines how
S, =0.45 x S, much bending stress is generated. In the case of buried
pipelines, the end condition-the freedom of movement in the
where S, =longitudinal stress and S,= tangential stress. longitudinal direction-+ dependent on the amount of pipe-to-
Longitudinal stresses also occur as a result of differential soil bonding and on the pipeline configuration (nearby bends or
temperatures. These stresses can be calculated from: valves may act as anchors to restrict movements).
A compressive bending reduces the longitudinal stress
0 temp =-a (AT) X E induced by pressure. A tensile bending stress is directly addi-
where tive to the longitudinal stress induced by pressure. In general,
0 temp = temperature-induced longitudinal stress hoop stresses are independent from longitudinal stresses. This
a = linear coefficient of expansion means that the most severe stress will govern-the stresses are
AT = temperature change not additive. A third category of pipe stresses is radial stress.
E = modulus of elasticity of pipe material. Radial stresses are usually considered to be negligible in com-
parison with hoop and longitudinal stresses.
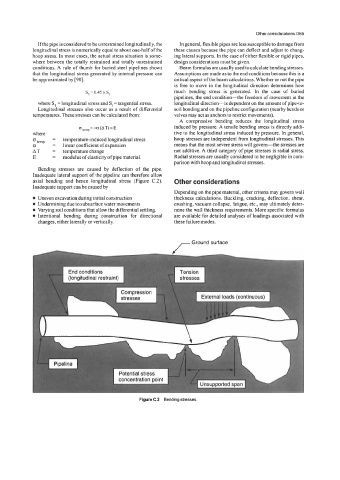
Bending stresses are caused by deflection of the pipe.
Inadequate lateral support of the pipeline can therefore allow
axial bending and hence longitudinal stress (Figure C.2). Other considerations
Inadequate support can be caused by
Depending on the pipe material, other criteria may govern wall
Uneven excavation during initial construction thickness calculations. Buckling, cracking, deflection, shear,
Undermining due to subsurface water movements crushing, vacuum collapse, fatigue, etc., may ultimately deter-
Varying soil conditions that allow the differential settling. mine the wall thickness requirements. More specific formulas
Intentional bending during construction for directional are available for detailed analyses of loadings associated with
changes, either laterally or vertically. these failure modes.
Figure C.2 Bending stresses