Page 88 - Pipeline Risk Management Manual Ideas, Techniques, and Resources
P. 88
4/66 Corrosion index
and the enclosed carrier pipe are beneath the ground, atmos- Ground/air interface As with the aidwater interface, the
pheric corrosion can be the prime corrosion mechanism. A vent groundair interface can be harsh from a corrosion standpoint.
pipe provides a path between the casing annular space and the This is the point at which the pipe enters and leaves the ground
atmosphere. In casings, the carrier pipe is often electrically (or is lying on the ground). The harshness is caused in part by
connected to the casing pipe, despite efforts to prevent it. This the potential for trapping moisture against the pipe (creating a
occurs either through direct metallic contact or through a waterlair interface). Soil movements due to changing moisture
higher resistance connection such as water in the casing. When content, freezing, etc., can also damage pipe coating, exposing
this connection is made, it is nearly impossible to control the bare metal to the electrolyte.
direction ofthe electrochemical reaction, or even to know accu-
rately what is happening in the casing. The worst situation Other exposures The above cases should cover the range of
occurs when the carrier pipeline becomes an anode to the cas- worst case exposures for steel pipe exposed to the atmosphere.
ing pipe, meaning the carrier pipe loses metal as the casing pipe One of the above situations must exist for any aboveground pip-
gains ions. Even without an electrical connection, the carrier ing; the pipe is either supported and/or it has one of the listed
pipe is subject to atmospheric corrosion, especially as the cas- interfaces. A situation may exist however, in which a non-steel
ing becomes filled with water and then later dries out (an pipe is not subject to degradation by any of the oxidation con-
aidwater interface). The inability for direct observation or even tributors listed. A plastic pipe may not be affected by any water
reliable inference techniques causes this scenario to rate high or air or even chemical contact and yet may become brittle (and
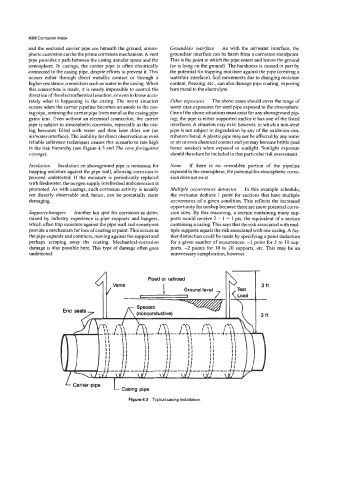
in the risk hierarchy (see Figure 4.3 and The case for/against hence weaker) when exposed to sunlight. Sunlight exposure
casings). should therefore be included in that particular risk assessment.
Insulation Insulation on aboveground pipe is notorious for None If there is no corrodible portion of the pipeline
trapping moisture against the pipe wall, allowing corrosion to exposed to the atmosphere, the potential for atmospheric corro-
proceed undetected. If the moisture is periodically replaced sion does not exist.
with freshwater, the oxygen supply is refreshed and corrosion is
promoted. As with casings, such corrosion activity is usually Multiple occurrences detmctor In this example schedule,
not directly observable and, hence, can be potentially more the evaluator deducts 1 point for sections that have multiple
damaging. occurrences of a given condition. This reflects the increased
opportunity for mishap because there are more potential corro-
Supportshangers Another hot spot for corrosion as deter- sion sites. By this reasoning, a section containing many sup-
mined by industry experience is pipe supports and hangers, ports would receive 2 - 1 = 1 pts, the equivalent of a section
which often trap moisture against the pipe wall and sometimes containing a casing. This says that the risk associated with mul-
provide a mechanism for loss of coating or paint. This occurs as tiple supports equals the risk associated with one casing. A fur-
the pipe expands and contracts, moving against the support and ther distinction could be made by specifying a point deduction
perhaps scraping away the coating. Mechanical-corrosion for a given number of occurrences: -1 point for 5 to 10 sup-
damage is also possible here. This type of damage often goes ports, -2 points for 10 to 20 supports, etc. This may be an
undetected. unnecessary complication, however.
Figure 4.3 Typical casing installation.