Page 230 - Pipeline Rules of Thumb Handbook
P. 230
Corrosion/Coatings 217
current that can be collected by the pipeline without exceed- can be applied along the pipeline from A to C and from
ing the disbonding limit. The lower limit is the minimum D to F.
amount of current that can be collected by the pipeline to When the earth current can reverse polarity, as with the
keep it above the corrosion limit. Pacific Northwest (PNW)-Pacific Southwest (PSW) intertie,
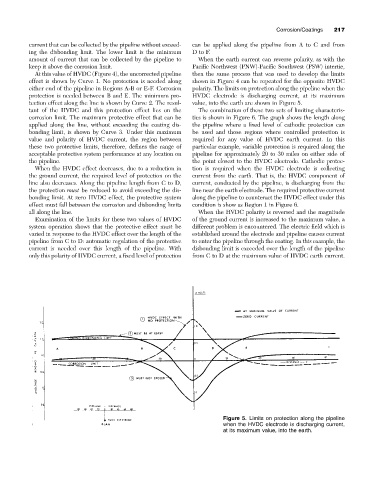
At this value of HVDC (Figure 4), the uncorrected pipeline then the same process that was used to develop the limits
effect is shown by Curve 1. No protection is needed along shown in Figure 4 can be repeated for the opposite HVDC
either end of the pipeline in Regions A-B or E-F. Corrosion polarity. The limits on protection along the pipeline when the
protection is needed between B and E. The minimum pro- HVDC electrode is discharging current, at its maximum
tection effect along the line is shown by Curve 2. The resul- value, into the earth are shown in Figure 5.
tant of the HVDC and this protection effect lies on the The combination of these two sets of limiting characteris-
corrosion limit. The maximum protective effect that can be tics is shown in Figure 6. The graph shows the length along
applied along the line, without exceeding the coating dis- the pipeline where a fixed level of cathodic protection can
bonding limit, is shown by Curve 3. Under this maximum be used and those regions where controlled protection is
value and polarity of HVDC current, the region between required for any value of HVDC earth current. In this
these two protective limits, therefore, defines the range of particular example, variable protection is required along the
acceptable protective system performance at any location on pipeline for approximately 20 to 30 miles on either side of
the pipeline. the point closest to the HVDC electrode. Cathodic protec-
When the HVDC effect decreases, due to a reduction in tion is required when the HVDC electrode is collecting
the ground current, the required level of protection on the current from the earth. That is, the HVDC component of
line also decreases. Along the pipeline length from C to D, current, conducted by the pipeline, is discharging from the
the protection must be reduced to avoid exceeding the dis- line near the earth electrode. The required protective current
bonding limit. At zero HVDC effect, the protective system along the pipeline to counteract the HVDC effect under this
effect must fall between the corrosion and disbonding limits condition is show as Region 1 in Figure 6.
all along the line. When the HVDC polarity is reversed and the magnitude
Examination of the limits for these two values of HVDC of the ground current is increased to the maximum value, a
system operation shows that the protective effect must be different problem is encountered. The electric field which is
varied in response to the HVDC effect over the length of the established around the electrode and pipeline causes current
pipeline from C to D: automatic regulation of the protective to enter the pipeline through the coating. In this example, the
current is needed over this length of the pipeline. With disbonding limit is exceeded over the length of the pipeline
only this polarity of HVDC current, a fixed level of protection from C to D at the maximum value of HVDC earth current.
Figure 5. Limits on protection along the pipeline
when the HVDC electrode is discharging current,
at its maximum value, into the earth.