Page 299 - Pipelines and Risers
P. 299
212 Chapter I5
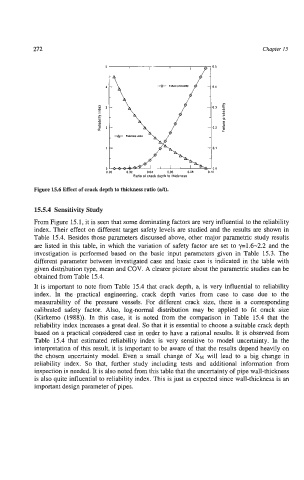
Figure 15.6 Effect of crack depth to thickness ratio (ah).
15.5.4 Sensitivity Study
From Figure 15.1, it is seen that some dominating factors are very influential to the reliability
index. Their effect on different target safety levels are studied and the results are shown in
Table 15.4. Besides those parameters discussed above, other major parametric study results
are listed in this table, in which the variation of safety factor are set to ~1.6-2.2 and the
invcstigation is pcrformed based on the basic input parameters given in Table 15.3. The
different parameter between investigated case and basic case is indicated in the table with
given distribution type, mean and COV. A clearer picture about the parametric studies can be
obtained from Table 15.4.
It is important to note from Table 15.4 that crack depth, a, is very influential to reliability
index. In the'practical engineering, crack depth varies from case to case due to the
measurability of the pressure vessels. For different crack size, there is a corresponding
calibrated safety factor. Also, log-normal distribution may be applied to fit crack size
(Kirkemo (1988)). In this case, it is noted from the comparison in Table 15.4 that the
reliability index increases a great deal. So that it is essential to choose a suitable crack depth
based on a practical considered case in order to have a rational results. It is observed from
Table 15.4 that estimated reliability index is very sensitive to model uncertainty. In the
interpretation of this result, it is important to be aware of that the results depend heavily on
the chosen uncertainty model. Even a small change of XM will lead to a big change in
reliability index. So that, further study including tests and additional information from
inspection is needed. It is also noted from this table that the uncertainty of pipe wall-thickness
is also quite influential to reliability index. This is just as expected since wall-thickness is an
important design parameter of pipes.