Page 467 - Pipelines and Risers
P. 467
434 Chapter 23
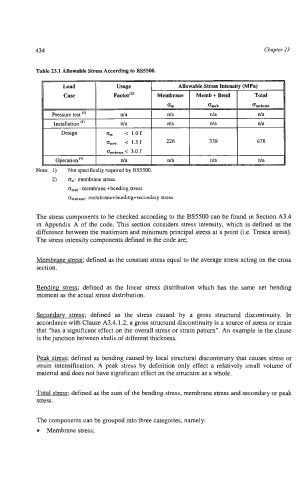
Table 23.1 Allowable Stress According to BS5500.
I :: I Factor"' Allowable Stress Intensity (MPa)
Usage
Total
Pressure test (I) I n/a
Installation (I) I n/a
Design
om* < 1.5 f
Note: 1) Not specifically required by BS5500.
2) om- membrane stress
oM - membrane +bending stress
membrane+bending+secondary stress
~ ~ m + b + ~ ~ -
The stress components to be checked according to the BS5500 can be found in Section A3.4
in Appendix A of the code. This section considers stress intensity, which is defined as the
difference between the maximum and minimum principal stress at a point (Le. Tresca stress).
The stress intensity components defined in the code are;
Membrane stress; defined as the constant stress equal to the average stress acting on the cross
section.
Bending stress; defined as the linear stress distribution which has the same net bending
moment as the actual stress distribution.
Secondarv stress; defined as the stress caused by a gross structural discontinuity. In
accordance with Clause A3.4.1.2, a gross structural discontinuity is a source of stress or strain
that "has a significant effect on the overall stress or strain pattern". An example in the clause
is the junction between shells of different thickness.
Peak stress; defined as bending caused by local structural discontinuity that causes stress or
strain intensification. A peak stress by definition only effect a relatively small volume of
material and does not have significant effect on the structure as a whole.
Total stress; defined as the sum of the bending stress, membrane stress and secondary or peak
stress.
The components can be grouped into three categories, namely:
Membrane stress;