Page 40 - Piston Engine-Based Power Plants
P. 40
32 Piston Engine-Based Power Plants
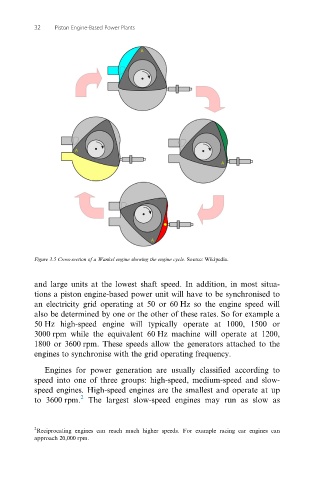
Figure 3.5 Cross-section of a Wankel engine showing the engine cycle. Source: Wikipedia.
and large units at the lowest shaft speed. In addition, in most situa-
tions a piston engine-based power unit will have to be synchronised to
an electricity grid operating at 50 or 60 Hz so the engine speed will
also be determined by one or the other of these rates. So for example a
50 Hz high-speed engine will typically operate at 1000, 1500 or
3000 rpm while the equivalent 60 Hz machine will operate at 1200,
1800 or 3600 rpm. These speeds allow the generators attached to the
engines to synchronise with the grid operating frequency.
Engines for power generation are usually classified according to
speed into one of three groups: high-speed, medium-speed and slow-
speed engines. High-speed engines are the smallest and operate at up
2
to 3600 rpm. The largest slow-speed engines may run as slow as
2 Reciprocating engines can reach much higher speeds. For example racing car engines can
approach 20,000 rpm.