Page 41 - Piston Engine-Based Power Plants
P. 41
Types of Reciprocating Engine 33
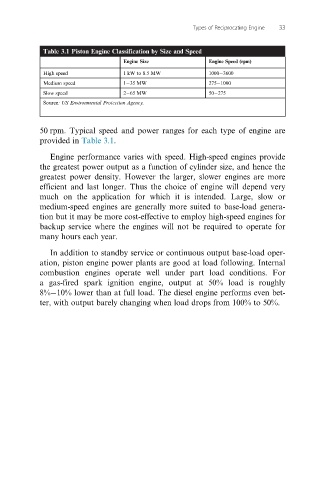
Table 3.1 Piston Engine Classification by Size and Speed
Engine Size Engine Speed (rpm)
High speed 1 kW to 8.5 MW 1000 3600
Medium speed 1 35 MW 275 1000
Slow speed 2 65 MW 50 275
Source: US Environmental Protection Agency.
50 rpm. Typical speed and power ranges for each type of engine are
provided in Table 3.1.
Engine performance varies with speed. High-speed engines provide
the greatest power output as a function of cylinder size, and hence the
greatest power density. However the larger, slower engines are more
efficient and last longer. Thus the choice of engine will depend very
much on the application for which it is intended. Large, slow or
medium-speed engines are generally more suited to base-load genera-
tion but it may be more cost-effective to employ high-speed engines for
backup service where the engines will not be required to operate for
many hours each year.
In addition to standby service or continuous output base-load oper-
ation, piston engine power plants are good at load following. Internal
combustion engines operate well under part load conditions. For
a gas-fired spark ignition engine, output at 50% load is roughly
8% 10% lower than at full load. The diesel engine performs even bet-
ter, with output barely changing when load drops from 100% to 50%.