Page 216 - Plant design and economics for chemical engineers
P. 216
188 PLANT DESIGN AND ECONOMICS FOR CHEMICAL ENGINEERS
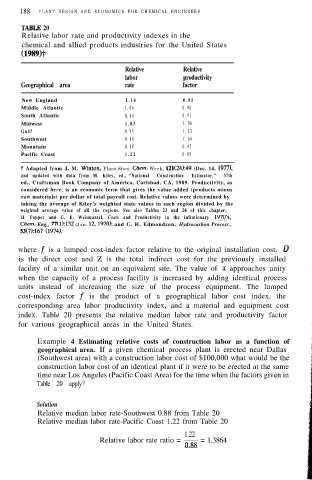
TABLE 20
Relative labor rate and productivity indexes in the
chemical and allied products industries for the United States
(1989Ft
Relative Relative
labor productivity
Geographical area rate factor
New England 1 . 1 4 0 . 9 5
Middle Atlantic 1.06 0.96
South Atlantic 0.84 0.91
Midwest 1 . 0 3 1.06
G u l f 0.95 1.22
Southwest 0.88 1.04
Mountain 0.88 0.97
Pacific Coast 1 . 2 2 0.89
t Adapted from J. M. Winton, Plant Sites, Chem. Week, 121(24):49 (Dec. 14, 1977),
and updated with data from M. Kiley, ed., “National Construction Estimator,” 37th
ed., Craftsman Book Company of America, Carlsbad, CA, 1989. Productivity, as
considered here, is an economic term that gives the value added (products minus
raw materials) per dollar of total payroll cost. Relative values were determined by
taking the average of Kiley’s weighted state values in each region divided by the
weighted average value of all the regions. See also Tables 23 and 24 of this chapter;
H. Popper and G. E. Weismantel, Costs and Productivity in the Inflationary 197O’s,
Chem. Eng., 77(1):132 (Jan. 12,197O); and C. H. Edmondson, Hydrocarbon Process.,
53(7):167 (1974).
where f is a lumped cost-index factor relative to the original installation cost. ‘D
is the direct cost and Z is the total indirect cost for the previously installed
facility of a similar unit on an equivalent site. The value of x approaches unity
when the capacity of a process facility is increased by adding identical process
units instead of increasing the size of the process equipment. The lumped
cost-index factor f is the product of a geographical labor cost index, the
corresponding area labor productivity index, and a material and equipment cost
index. Table 20 presents the relative median labor rate and productivity factor
for various geographical areas in the United States.
Example 4 Estimating relative costs of construction labor as a function of
geographical area. If a given chemical process plant is erected near Dallas
(Southwest area) with a construction labor cost of $100,000 what would be the
construction labor cost of an identical plant if it were to be erected at the same
time near Los Angeles (Pacific Coast Area) for the time when the factors given in
Table 20 apply?
Solution
Relative median labor rate-Southwest 0.88 from Table 20
Relative median labor rate-Pacific Coast 1.22 from Table 20
1.22
Relative labor rate ratio = 0 = 1.3864