Page 195 - Plant-Based Remediation Processes
P. 195
10 Phytostabilization as Soil Remediation Strategy 187
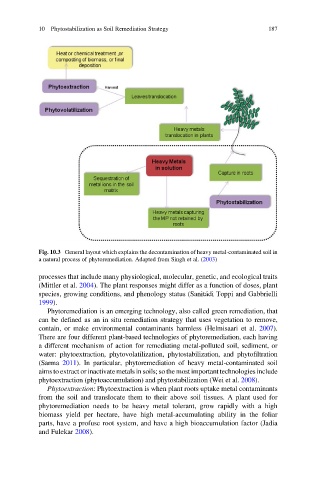
Fig. 10.3 General layout which explains the decontamination of heavy metal-contaminated soil in
a natural process of phytoremediation. Adapted from Singh et al. (2003)
processes that include many physiological, molecular, genetic, and ecological traits
(Mittler et al. 2004). The plant responses might differ as a function of doses, plant
species, growing conditions, and phenology status (Sanita ´di Toppi and Gabbrielli
1999).
Phytoremediation is an emerging technology, also called green remediation, that
can be defined as an in situ remediation strategy that uses vegetation to remove,
contain, or make environmental contaminants harmless (Helmisaari et al. 2007).
There are four different plant-based technologies of phytoremediation, each having
a different mechanism of action for remediating metal-polluted soil, sediment, or
water: phytoextraction, phytovolatilization, phytostabilization, and phytofiltration
(Sarma 2011). In particular, phytoremediation of heavy metal-contaminated soil
aims to extract or inactivate metals in soils; so the most important technologies include
phytoextraction (phytoaccumulation) and phytostabilization (Wei et al. 2008).
Phytoextraction: Phytoextraction is when plant roots uptake metal contaminants
from the soil and translocate them to their above soil tissues. A plant used for
phytoremediation needs to be heavy metal tolerant, grow rapidly with a high
biomass yield per hectare, have high metal-accumulating ability in the foliar
parts, have a profuse root system, and have a high bioaccumulation factor (Jadia
and Fulekar 2008).