Page 288 - Plastics Engineering
P. 288
Processing of Plastics 27 1
Mould
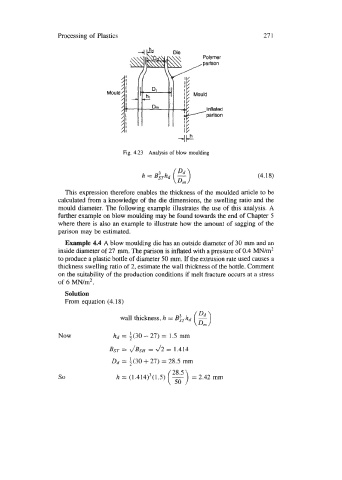
Fig. 4.23 Analysis of blow moulding
(4.18)
This expression therefore enables the thickness of the moulded article to be
calculated from a knowledge of the die dimensions, the swelling ratio and the
mould diameter. The following example illustrates the use of this analysis. A
further example on blow moulding may be found towards the end of Chapter 5
where there is also an example to illustrate how the amount of sagging of the
parison may be estimated.
Example 4.4 A blow moulding die has an outside diameter of 30 mm and an
inside diameter of 27 mm. The parison is inflated with a pressure of 0.4 MN/m2
to produce a plastic bottle of diameter 50 mm. If the extrusion rate used causes a
thickness swelling ratio of 2, estimate the wall thickness of the bottle. Comment
on the suitability of the production conditions if melt fracture occurs at a stress
of 6 MN/m2.
Solution
From equation (4.18)
wall thickness, h = B&hd (2)
Now hd = :(30 - 27) = 1.5 mm
so h = (1.414)3(1.5) - = 2.42 mm
(2::>