Page 93 - Polymer-based Nanocomposites for Energy and Environmental Applications
P. 93
Preparation and properties of nanopolymer advanced composites: A review 69
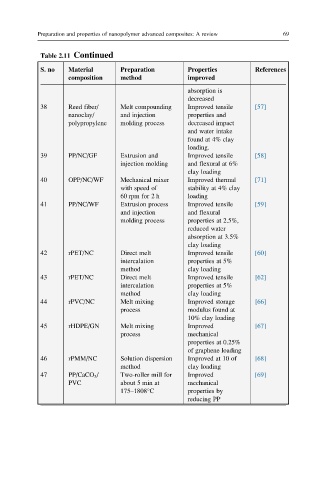
Table 2.11 Continued
S. no Material Preparation Properties References
composition method improved
absorption is
decreased
38 Reed fiber/ Melt compounding Improved tensile [57]
nanoclay/ and injection properties and
polypropylene molding process decreased impact
and water intake
found at 4% clay
loading.
39 PP/NC/GF Extrusion and Improved tensile [58]
injection molding and flexural at 6%
clay loading
40 OPP/NC/WF Mechanical mixer Improved thermal [71]
with speed of stability at 4% clay
60 rpm for 2 h loading
41 PP/NC/WF Extrusion process Improved tensile [59]
and injection and flexural
molding process properties at 2.5%,
reduced water
absorption at 3.5%
clay loading
42 rPET/NC Direct melt Improved tensile [60]
intercalation properties at 5%
method clay loading
43 rPET/NC Direct melt Improved tensile [62]
intercalation properties at 5%
method clay loading
44 rPVC/NC Melt mixing Improved storage [66]
process modulus found at
10% clay loading
45 rHDPE/GN Melt mixing Improved [67]
process mechanical
properties at 0.25%
of graphene loading
46 rPMM/NC Solution dispersion Improved at 10 of [68]
method clay loading
47 PP/CaCO 3 / Two-roller mill for Improved [69]
PVC about 5 min at mechanical
175–1808°C properties by
reducing PP