Page 79 - Power Electronics Handbook
P. 79
72 Thennal design
is that the heat can be removed to a location remote from the power
semiconductor before it is dissipated.
A heat pipe is a device which is sometimes used with power
semiconductors to conduct the heat away from a component? mounted in
an inaccessible position, to a larger, remote dissipater. A metal bar
conducts heat very inefficiently: for example, conducting 1 kW of heat in a
solid copper rod of 1.5 cm diameter over a 30cm length would give about
800°C difference between its ends. A heat pipe of the same dimensions
would give a 2°C difference, therefore it is much more efficient.
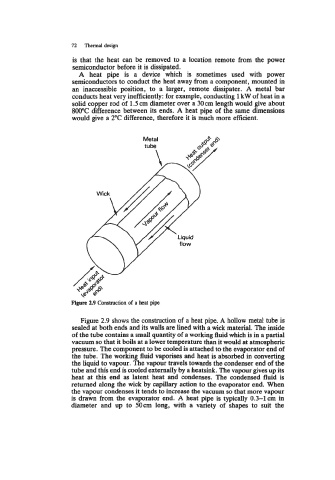
Figure 2.9 Construction of a heat pipe
Figure 2.9 shows the construction of a heat pipe. A hollow metal tube is
sealed at both ends and its walls are lined with a wick material. The inside
of the tube contains a small quantity of a working fluid which is in a partial
vacuum so that it boils at a lower temperature than it would at atmospheric
pressure. The component to be cooled is attached to the evaporator end of
the tube. The working fluid vaporises and heat is absorbed in converting
the liquid to vapour. The vapour travels towards the condenser end of the
tube and this end is cooled externally by a heatsink. The vapour gives up its
heat at this end as latent heat and condenses. The condensed fluid is
returned along the wick by capillary action to the evaporator end. When
the vapour condenses it tends to increase the vacuum so that more vapour
is drawn from the evaporator end. A heat pipe is typically 0.3-1cm in
diameter and up to 50cm long, with a variety of shapes to suit the