Page 135 - Power Quality in Electrical Systems
P. 135
Methods for Correction of Power-Quality Problems 117
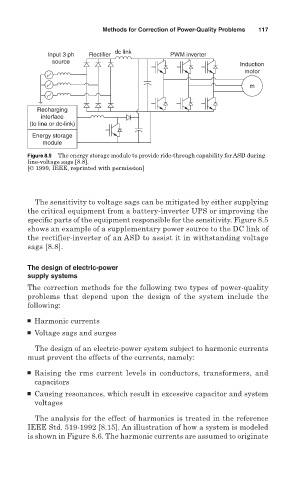
dc link
Input 3 ph Rectifier PWM inverter
source
Induction
motor
m
Recharging
interface
(to line or dc-link)
Energy storage
module
Figure 8.5 The energy storage module to provide ride-through capability for ASD during
line-voltage sags [8.8].
[© 1999, IEEE, reprinted with permission]
The sensitivity to voltage sags can be mitigated by either supplying
the critical equipment from a battery-inverter UPS or improving the
specific parts of the equipment responsible for the sensitivity. Figure 8.5
shows an example of a supplementary power source to the DC link of
the rectifier-inverter of an ASD to assist it in withstanding voltage
sags [8.8].
The design of electric-power
supply systems
The correction methods for the following two types of power-quality
problems that depend upon the design of the system include the
following:
■ Harmonic currents
■ Voltage sags and surges
The design of an electric-power system subject to harmonic currents
must prevent the effects of the currents, namely:
■ Raising the rms current levels in conductors, transformers, and
capacitors
■ Causing resonances, which result in excessive capacitor and system
voltages
The analysis for the effect of harmonics is treated in the reference
IEEE Std. 519-1992 [8.15]. An illustration of how a system is modeled
is shown in Figure 8.6. The harmonic currents are assumed to originate