Page 167 - Power Quality in Electrical Systems
P. 167
Dynamic Voltage Compensators 149
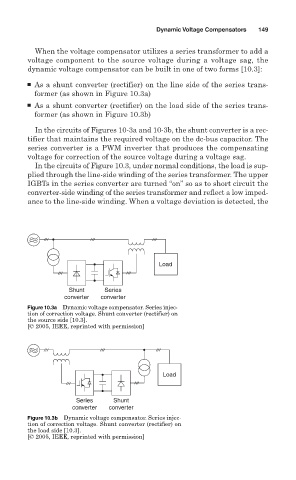
When the voltage compensator utilizes a series transformer to add a
voltage component to the source voltage during a voltage sag, the
dynamic voltage compensator can be built in one of two forms [10.3]:
■ As a shunt converter (rectifier) on the line side of the series trans-
former (as shown in Figure 10.3a)
■ As a shunt converter (rectifier) on the load side of the series trans-
former (as shown in Figure 10.3b)
In the circuits of Figures 10-3a and 10-3b, the shunt converter is a rec-
tifier that maintains the required voltage on the dc-bus capacitor. The
series converter is a PWM inverter that produces the compensating
voltage for correction of the source voltage during a voltage sag.
In the circuits of Figure 10.3, under normal conditions, the load is sup-
plied through the line-side winding of the series transformer. The upper
IGBTs in the series converter are turned “on” so as to short circuit the
converter-side winding of the series transformer and reflect a low imped-
ance to the line-side winding. When a voltage deviation is detected, the
Load
Shunt Series
converter converter
Figure 10.3a Dynamic voltage compensator. Series injec-
tion of correction voltage. Shunt converter (rectifier) on
the source side [10.3].
[© 2005, IEEE, reprinted with permission]
Load
Series Shunt
converter converter
Figure 10.3b Dynamic voltage compensator. Series injec-
tion of correction voltage. Shunt converter (rectifier) on
the load side [10.3].
[© 2005, IEEE, reprinted with permission]