Page 244 - Practical Design Ships and Floating Structures
P. 244
2 I9
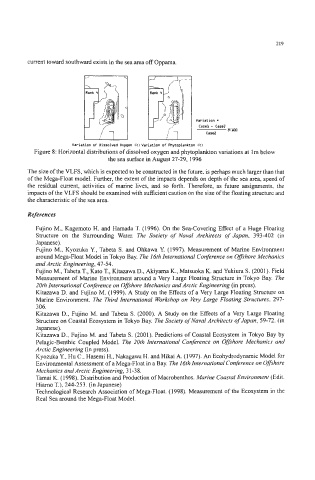
current toward southward exists in the sea area off Oppama.
Variation =
Case1 - Case.?
*MOO
Case.?
Variation of Dissolved Oxygen (%) Variation of Phytoplankton (2)
Figure 8: Horizontal distributions of dissolved oxygen and phytoplankton variations at Im below
the sea surface in August 27-29, 1996
The size of the VLFS, which is expected to be constructed in the future, is perhaps much larger than that
of the Mega-Float model. Further, the extent of the impacts depends on depth of the sea area, speed of
the residual current, activities of marine lives, and so forth. Therefore, as future assignments. the
impacts of the VLFS should be examined with sufficient caution on the size of the floating structurc and
the characteristic of the sea area.
References
Fujino M., Kagemoto H. and Hamada T. (1996). On the Sea-Covering Effect of a Huge Floating
Structure on the Surrounding Water. The Society of Naval Architects of Japan, 393-402 (in
Japanese).
Fujino M., Kyozuka Y., Tabeta S. and Ohkawa Y. (1997). Measurement of Marine Environment
around Mega-Float Model in Tokyo Bay. The 16th International Conference on Offshore Mechanics
and Arctic Engineering, 47-54.
Fujino M., Tabeta T., Kato T., Kitazawa D., Akiyama K., Matsuoka K. and Yukiura S. (2001). Field
Measurement of Marine Environment around a Very Large Floating Structure in Tokyo Bay. The
20th International Conference on Offshore Mechanics and Arctic Engineering (in press).
Kitazawa D. and Fujino M. (1999). A Study on the Effects of a Very Large Floating Structure on
Marine Environment. The Third International Workshop on Very Large Floating Structures. 297-
306.
Kitazawa D., Fujino M. and Tabeta S. (2000). A Study on the Effects of a Very Large Floating
Structure on Coastal Ecosystem in Tokyo Bay. The Society of Naval Architects of Japan, 59-72. (in
Japanese).
Kitazawa D., Fujino M. and Tabeta S. (2001). Predictions of Coastal Ecosystem in Tokyo Bay by
Pelagic-Benthic Coupled Model. The 20th International Conference on Offihore Mechanics and
Arctic Engineering (in press).
Kyozuka Y., Hu C.. Hasemi H., Nakagawa H. and Hikai A. (1997). An Ecohydrodynamic Model for
Environmental Assessment of a Mega-Float in a Bay. The I6th International Conference on Qfshore
Mechanics and Arctic Engineering, 3 1-38.
Tamai K. (1 998). Distribution and Production of Macrobenthos. Marine Coastal Environment (Edit.
Hiamo T.), 244-253. (in Japanese)
Technological Research Association of Mega-Float. (1 998). Measurement of the Ecosystem in the
Real Sea around the Mega-Float Model.