Page 386 - Practical Design Ships and Floating Structures
P. 386
361
evaluation.
The modelling is based on a definition of the relationships between the elements of the product, the
available or planned resources and the necessary operations as shown in Figure 2. By these definitions
a scalable model can be obtained (electronic Bill of Process - eBoP).
For the use of this model a detailed analysis of the plant and the production process is necessary. The
analysis in existing factories leads to an evaluation process, which also reveals the weak and strong
points of the production line and the associated processes. The modelling leads additionally to
considerations related to the necessity of single process steps or the avoiding of them. As a
consequence of the introduction of simulation a deeper understanding of the complex relationship
pattern of the many instances is generated.
The same simulation methods can be used in designing new or refurbishing existing plants. The
decision making by the investor is then based on facts rather than promises or assumptions
Once the plant is modelled in the indicated manner the production process for an individual product
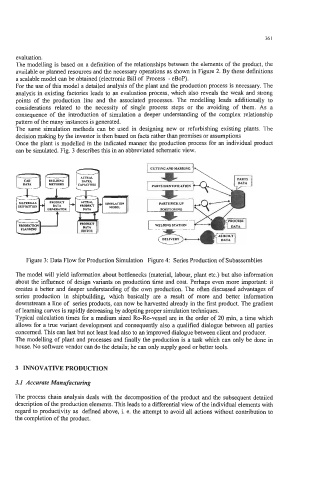
can be simulated. Fig. 3 describes this in an abbreviated schematic view.
CUTTINGANDMARKING \
L J
METHODS CAPACIllES PARTS IDENTIFICATION
PARTS PICK UP
POSITIONING
1
Figure 3: Data Flow for Production Simulation Figure 4: Series Production of Subassemblies
The model will yield information about bottlenecks (material, labour, plant etc.) but also information
about the influence of design variants on production time and cost. Perhaps even more important: it
creates a better and deeper understanding of the own production. The often discussed advantages of
series production in shipbuilding, which basically are a result of more and better information
downstream a line of series products, can now be harvested already in the first product. The gradient
of learning curves is rapidly decreasing by adopting proper simulation techniques.
Typical calculation times for a medium sized Ro-Ro-vessel are in the order of 20 min, a time which
allows for a true variant development and consequently also a qualified dialogue between all parties
concerned. This can last but not least lead also to an improved dialogue between client and producer.
The modelling of plant and processes and finally the production is a task which can only be done in
house. No software vendor can do the details; he can only supply good or better tools.
3 INNOVATIVE PRODUCTION
3.1 Accurate Manufacturing
The process chain analysis deals with the decomposition of the product and the subsequent detailed
description of the production elements. This leads to a differential view of the individual elements with
regard to productivity as defined above, i. e. the attempt to avoid all actions without contribution to
the completion of the product.