Page 516 - Practical Design Ships and Floating Structures
P. 516
49 1
3.2 Seale Effect of Water Flow just behind a Transom Stern
Figure 3 shows scale effect of water flow just behind the transom stem of M.S.NO.CA at F, = 0.25
on Full-2 estimated by our methodt2. Reliability of Figure 3 can be understood by Figure 4. Figure 4
compares estimated water flow with observed water surface on Full-1 and Full-2 for M.S.NO. CA. We
can see from Figure 4 that the estimated water flow can explain fairly well the difference of
forward-oriented wave breaking and that of remained following waves seen between the two observed
water surfaces. Figure 5 summarizes change with Reynolds number Re = voLwL / v of G/LwL, yJ LWL
and HJ LWL for each of the two conditions, where H, is remained following wave height. S/ Llr,,.
decreases with increase of model ship size. This causes decrease of yc/ LWL and also increase of H,,i
LwI..
We can also see by comparing above estimated data on Full-1 with those on Full-2 that such tendency
becomes more remarkable on condition with higher value of y,/ LWL.
Regarding H,,J LWL, above estimated tendency is seen in the wave heights measured on two similar
model ships with Lpp of 2m and 10m by Miyata et a].’.
3.3 Scale Effect of the Resistance due fo Stern Waves Including Forward-oriented Wave Breaking
just behind a Transom Stern
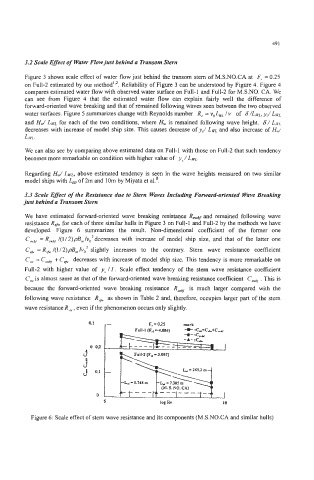
We have estimated forward-oriented wave breaking resistance Rwb. and remained following wave
resistance RS&. for each of three similar hulls in Figure 3 on Full-1 and Full-2 by the methods we have
developed. Figure 6 summarizes the result. Non-dimensional coefficient of the former one
C,,,,,, = R,,, /(1/2)pB,IvO2decreases with increase of model ship size, and that of the latter one
C, = R, /(1/ 2)pB,,, IvO2 slightly increases to the contrary. Stem wave resistance coefficient
C,w = Cwb, + C, decreases with increase of model ship size. This tendency is more remarkable on
Full-2 with higher value of y, /I. Scale effect tendency of the stem wave resistance coefficient
.
C, is almost same as that of the forward-oriented wave breaking resistance coefficient C, This is
because the forward-oriented wave breaking resistance R,, is much larger compared with the
following wave resistance R, as shown in Table 2 and, therefore, occupies larger part of the stem
wave resistance R,w, even if the phenomenon occurs only slightly.
0 0.2
E
u-
s
t
E
u 0.1
0
5 log Re 10
Figure 6: Scale effect of stem wave resistance and its components (M.S.NO.CA and similar hulls)