Page 165 - Practical Power System and Protective Relays Commissioning
P. 165
Power System Fault Analysis Chapter | 16 165
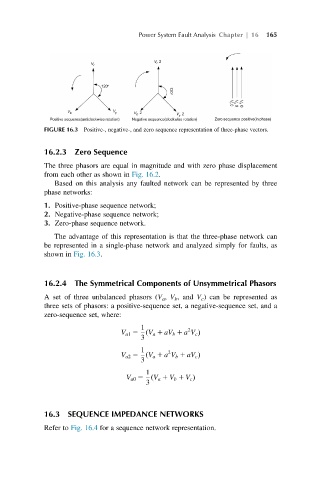
FIGURE 16.3 Positive-, negative-, and zero sequence representation of three-phase vectors.
16.2.3 Zero Sequence
The three phasors are equal in magnitude and with zero phase displacement
from each other as shown in Fig. 16.2.
Based on this analysis any faulted network can be represented by three
phase networks:
1. Positive-phase sequence network;
2. Negative-phase sequence network;
3. Zero-phase sequence network.
The advantage of this representation is that the three-phase network can
be represented in a single-phase network and analyzed simply for faults, as
shown in Fig. 16.3.
16.2.4 The Symmetrical Components of Unsymmetrical Phasors
A set of three unbalanced phasors (V a , V b , and V c ) can be represented as
three sets of phasors: a positive-sequence set, a negative-sequence set, and a
zero-sequence set, where:
1
2
V a1 5 ðV a 1 aV b 1 a V c Þ
3
1
2
V a2 5 ðV a 1 a V b 1 aV c Þ
3
1
V a0 5 ðV a 1 V b 1 V c Þ
3
16.3 SEQUENCE IMPEDANCE NETWORKS
Refer to Fig. 16.4 for a sequence network representation.