Page 40 - Practical Power System and Protective Relays Commissioning
P. 40
36 Practical Power System and Protective Relays Commissioning
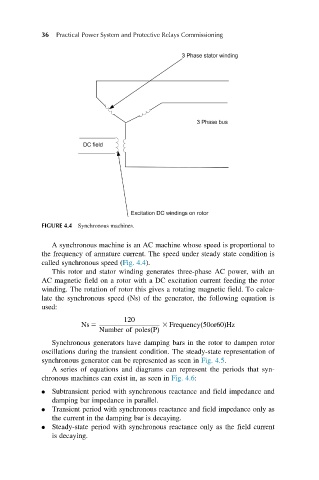
FIGURE 4.4 Synchronous machines.
A synchronous machine is an AC machine whose speed is proportional to
the frequency of armature current. The speed under steady state condition is
called synchronous speed (Fig. 4.4).
This rotor and stator winding generates three-phase AC power, with an
AC magnetic field on a rotor with a DC excitation current feeding the rotor
winding. The rotation of rotor this gives a rotating magnetic field. To calcu-
late the synchronous speed (Ns) of the generator, the following equation is
used:
120
Ns 5 3 Frequency 50or60ÞHz
ð
Number of poles PðÞ
Synchronous generators have damping bars in the rotor to dampen rotor
oscillations during the transient condition. The steady-state representation of
synchronous generator can be represented as seen in Fig. 4.5.
A series of equations and diagrams can represent the periods that syn-
chronous machines can exist in, as seen in Fig. 4.6:
Subtransient period with synchronous reactance and field impedance and
damping bar impedance in parallel.
Transient period with synchronous reactance and field impedance only as
the current in the damping bar is decaying.
Steady-state period with synchronous reactance only as the field current
is decaying.