Page 31 - Principles of Catalyst Development
P. 31
CATALYTIC FUNCTIONS 17
\ I
\ 1
\ I
\ 1
\ 1
\ 1
\ I
, I
N2 ADSORPTION \/ NH3 DESORPTION
CONTROLS I, CONTROLS
~
W
l-
e:(
a:
ENTHALPY OF ADSORPTION
N2 OR NH3
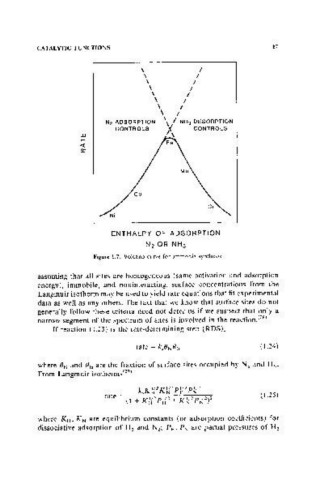
Figure 1.7. Volcano curve for ammonia synthesis.
assuming that all sites are homogeneous (same activation and adsorption
energy), immobile, and noninteracting, surface concentrations from the
Langmuir isotherm may be used to yield rate equations that fit experimental
data as well as any others. The fact that we know that surface sites do not
generally follow these criteria need not deter us if we suspect that only a
narrow segment of the spectrum of sites is involved in the reaction. (28)
If reaction (1.23) is the rate-determining step (RDS),
(1.24)
where ON and OH are the fraction of surface sites occupied by Ns and Hs.
From Langmuir isotherms(29)
(1.25 )
where K H , KN are equilibrium constants (or adsorption coefficients) for
dissociative adsorption of H2 and N 2 ; PH, PN are partial pressures of H2