Page 126 - Process Equipment and Plant Design Principles and Practices by Subhabrata Ray Gargi Das
P. 126
5.3 Multi-stream problem 123
and
CP h CP h CP h
2 3
1 ðTS h TS c Þ 1 þ ðDT min Þ
CP c CP c CP c
ln 4 5 (5.10)
A ex ¼
CP h U ex ðDT min Þ
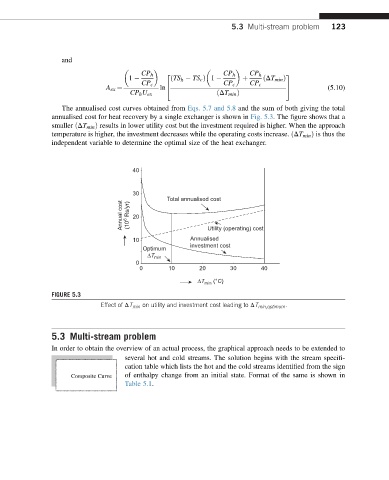
The annualised cost curves obtained from Eqs. 5.7 and 5.8 and the sum of both giving the total
annualised cost for heat recovery by a single exchanger is shown in Fig. 5.3. The figure shows that a
smaller ðDT min Þ results in lower utility cost but the investment required is higher. When the approach
temperature is higher, the investment decreases while the operating costs increase. ðDT min Þ is thus the
independent variable to determine the optimal size of the heat exchanger.
40
30
Total annualised cost
Annual cost (10 6 Rs/yr) 20
Utility (operating) cost
10 Annualised
investment cost
Optimum
ΔT min
0
0 10 20 30 40
ΔT min (°C)
FIGURE 5.3
Effect of DT min on utility and investment cost leading to DT min;optimum .
5.3 Multi-stream problem
In order to obtain the overview of an actual process, the graphical approach needs to be extended to
several hot and cold streams. The solution begins with the stream specifi-
cation table which lists the hot and the cold streams identified from the sign
Composite Curve of enthalpy change from an initial state. Format of the same is shown in
Table 5.1.