Page 47 - Process Equipment and Plant Design Principles and Practices by Subhabrata Ray Gargi Das
P. 47
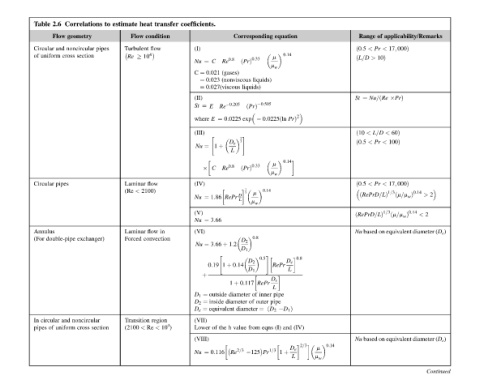
applicability/Remarks 17; 000Þ PrÞ 17; 000Þ 2 > 2 < Nu based on equivalent diameter (D e ) Nu based on equivalent diameter (D e ) Continued
of < Pr 10Þ > Nu=ðRe 60Þ < L=D 100Þ < Pr < Pr ðRePrD=LÞ 1=3 ðm=m w Þ 0:14 ðRePrD=LÞ 1=3 ðm=m w Þ 0:14
Range < ð0:5 ðL=D ¼ St < ð10 < ð0:5 < ð0:5
0:14
m m w
equation 0:14 m m w PrÞ 2 0:0225ðln 0:14 m m w RePr D e 0:8 L L pipe pipe D 1 Þ (IV) and (I) 1 þ D e 2=3 L
Corresponding ðPrÞ 0:33 liquids) liquids) ðPrÞ 0:505 exp 3 ðPrÞ 0:33 0:14 1 3 m m w D 2 0:8 D 1 D 2 0:5 # D 1 RePr D e 1 þ 0:117 inner of outer of ¼ðD 2 diameter eqns from 125 Pr 1=3
Re 0:8 (gases) (nonviscous 0.027(viscous Re 0:205 0:0225 ¼ D e 2 # 1 þ L Re 0:8 RePr D 1:86 L 3:66 3:66 þ 1:2 " 1 þ 0:14 diameter outside diameter inside equivalent value h the of Re 2=3 0:116
coefficients. (I) C ¼ Nu 0.021 ¼ C 0.023 ¼ ¼ (II) ¼ St E E where (III) " ¼ Nu C (IV) ¼ Nu (V) ¼ Nu (VI) ¼ Nu 0:19 þ ¼ D 1 ¼ D 2 ¼ D e (VII) Lower (VIII) ¼ Nu
transfer condition in convection region 10 4 ) <
heat Flow flow Turbulent 10 4 flow Laminar 2100) < flow Laminar Transition Re <
estimate Re (Re Forced (2100
to pipes section
Correlations geometry noncircular section exchanger) noncircular cross
2.6 Flow and cross uniform pipes double-pipe and circular uniform of
Table Circular of Circular Annulus (For In pipes