Page 300 - Process Modelling and Simulation With Finite Element Methods
P. 300
Coupling Variables Revisited 287
and it is seen to be linear. FEMLAB will not permit a zero size element at the
origin, so you need to specify an affine term. In mesh mode, specify, for
instance:
Mesh Mode: gl
Mesh size expression: 0.08+(x+0.08)*0.08
Which yields 98 nodes and 97 elements. Similarly,
Mesh Mode: 922
Which yields 2426 nodes and 4624 elements.
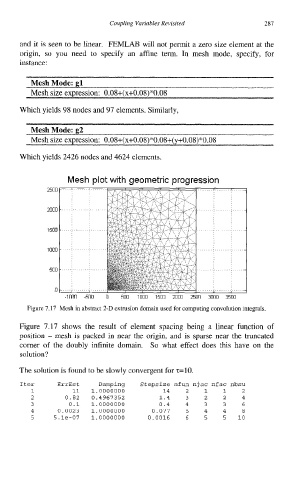
Mesh plot with geometric progression
Figure 7.17 Mesh in abstract 2-D extrusion domain used for computing convolution integrals.
Figure 7.17 shows the result of element spacing being a linear function of
position - mesh is packed in near the origin, and is sparse near the truncated
corner of the doubly infinite domain. So what effect does this have on the
solution?
The solution is found to be slowly convergent for %=lo.
Iter ErrEst Damping Stepsize nfun njac nfac nbsu
1 11 1.0000000 1 4 2 1 1 2
2 0.82 0.4967352 1.4 3 2 2 4
3 0.1 1.0000000 0.4 4 3 3 6
4 0.0023 1.0000000 0.077 5 4 4 8
5 5.le-07 1.0000000 0.0016 6 5 5 10