Page 94 - Programming the Photon Getting Started With the Internet of Things
P. 94
add multiple servos by creating different objects with different names and assign another
analog pin to it. In the loop(), the potentiometer is read and scaled down using the map()
function. The map() function takes one range of values and uses integer math to change it
to another range of values. This is a useful function when you need to limit values.
Map(value, fromLow, fromHigh, toLow, toHigh);
Once the value has been read and scaled, it is then written to the servo to fix its position
using a PWM pin to send the pulse. There is a short delay in the program just to make sure
that the servo has reached its intended position before another command is sent to the
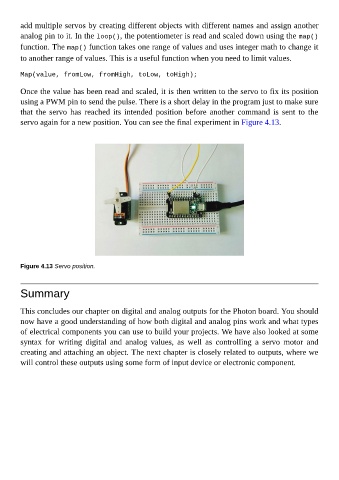
servo again for a new position. You can see the final experiment in Figure 4.13.
Figure 4.13 Servo position.
Summary
This concludes our chapter on digital and analog outputs for the Photon board. You should
now have a good understanding of how both digital and analog pins work and what types
of electrical components you can use to build your projects. We have also looked at some
syntax for writing digital and analog values, as well as controlling a servo motor and
creating and attaching an object. The next chapter is closely related to outputs, where we
will control these outputs using some form of input device or electronic component.