Page 14 - Radar Technology Encyclopedia
P. 14
4 absorber, magnetic absorber, Salisbury screen
impregnated with short metal fibers, are shown in Fig. A10.
SAL
Ref.: Bhattacharyya (1991), pp. 217, 218; K. Hatakeyama and T. Inui, “Elec-
tromagnetic Wave Absorber Using Ferrite Absorbing Materials Dis-
persed with Short Metal Fibers,” IEEE Trans. MAG-20, no. 5, Sept.
1984, pp. 126–1263.
Figure A11 The angular performance of m = e absorber for
r
r
different values of |me | (from Bhattacharyya, 1991, Fig. 4.68,
p. 215).
reduce surface currents (and so to suppress traveling and
creeping waves echoes) and use tapered resistive strips to
suppress edge diffraction returns. SAL
Ref.: Knott (1993), pp. 343–355.
Pyramidal absorber is the term sometimes used for a geo-
metric transition absorber with pyramidal profile. SAL
Ref.: Bhattacharyya (1991), p. 219.
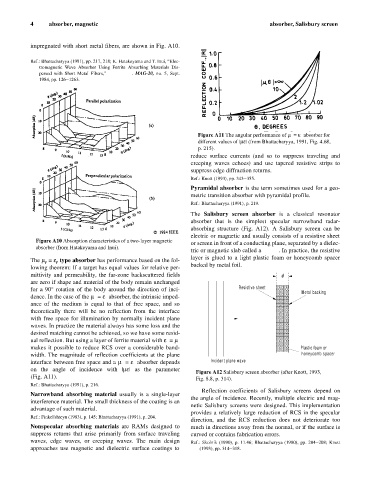
The Salisbury screen absorber is a classical resonator
absorber that is the simplest specular narrowband radar-
absorbing structure (Fig. A12). A Salisbury screen can be
electric or magnetic and usually consists of a resistive sheet
Figure A10 Absorption characteristics of a two-layer magnetic
or screen in front of a conducting plane, separated by a dielec-
absorber (from Hatakeyama and Inui).
tric or magnetic slab called a spacer. In practice, the resistive
layer is glued to a light plastic foam or honeycomb spacer
The m = e type absorber has performance based on the fol-
r r
lowing theorem: If a target has equal values for relative per- backed by metal foil.
mittivity and permeability, the far-zone backscattered fields d
are zero if shape and material of the body remain unchanged
for a 90° rotation of the body around the direction of inci- Resistive sheet
Metal backing
dence. In the case of the m = e absorber, the intrinsic imped-
r r
ance of the medium is equal to that of free space, and so
theoretically there will be no reflection from the interface
with free space for illumination by normally incident plane
waves. In practice the material always has some loss and the
desired matching cannot be achieved, so we have some resid-
ual reflection. But using a layer of ferrite material with e = m
r r
makes it possible to reduce RCS over a considerable band- Plastic foam or
width. The magnitude of reflection coefficients at the plane honeycomb spacer
interface between free space and a m = e absorber depends Incident plane wave
r r
on the angle of incidence with |me| as the parameter
Figure A12 Salisbury screen absorber (after Knott, 1993,
(Fig. A11). SAL
Fig. 8.8, p. 314).
Ref.: Bhattacharyya (1991), p. 216.
Reflection coefficients of Salisbury screens depend on
Narrowband absorbing material usually is a single-layer
the angle of incidence. Recently, multiple electric and mag-
interference material. The small thickness of the coating is an
netic Salisbury screens were designed. This implementation
advantage of such material. IAM
provides a relatively large reduction of RCS in the specular
Ref.: Finkel'shteyn (1983), p. 145; Bhattacharyya (1991), p. 204.
direction, and the RCS reduction does not deteriorate too
Nonspecular absorbing materials are RAMs designed to much in directions away from the normal, or if the surface is
suppress returns that arise primarily from surface traveling curved or contains fabrication errors. SAL
waves, edge waves, or creeping waves. The main design Ref.: Skolnik (1990), p. 11.46; Bhattacharyya (1980), pp. 204–208; Knott
approaches use magnetic and dielectric surface coatings to (1993), pp. 314–318.