Page 186 - Radar Technology Encyclopedia
P. 186
feed, beam-forming network feed, constrained 176
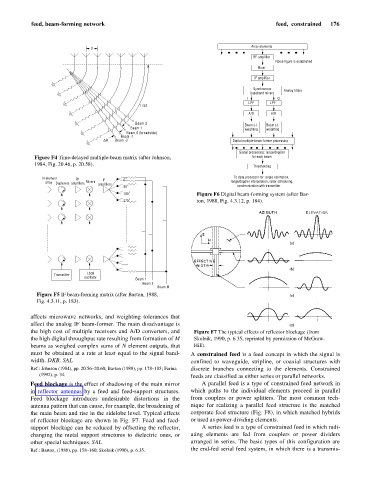
Array elements
d
RF amplifier
Noise figure is established
Mixer
IF amplifier
Synchronous Analog filters
baseband mixers
I Q
LPF LPF
1 rad
A/D A/D
Beam 2 Beam s.l. Beam s.l.
Beam 1 weighting weighting
Beam 0 (broadside)
Beam -1
Dq Beam -2 Digital multiple-beam-former processing
Signal processing: range/doppler
Figure F4 Time-delayed multiple-beam matrix (after Johnson, for each beam
1984, Fig. 20.46, p. 20.58). Thresholding
N-element Rf IF 0 o To data processor for: angle estimation,
array Duplexers amplifiers Mixers range/doppler interpolation, radar scheduling,
amplifiers o synchronization with transmitter
90
180 o Figure F6 Digital beam-forming system (after Bar-
o
270 ton, 1988, Fig. 4.3.12, p. 184).
Local
Transmitter
oscillator Beam 1
Beam 2
Beam M
Figure F5 IF beam-forming matrix (after Barton, 1988,
Fig. 4.3.11, p. 183).
affects microwave networks, and weighting tolerances that
affect the analog IF beam-former. The main disadvantage is
the high cost of multiple receivers and A/D converters, and Figure F7 The typical effects of reflector blockage (from
the high digital throughput rate resulting from formation of M Skolnik, 1990, p. 6.35, reprinted by permission of McGraw-
beams as weighed complex sums of N element outputs, that Hill).
must be obtained at a rate at least equal to the signal band- A constrained feed is a feed concept in which the signal is
width. DKB, SAL confined to waveguide, stripline, or coaxial structures with
Ref.: Johnson (1984), pp. 20.56–20.60; Barton (1988), pp. 178–185; Farina discrete branches connecting to the elements. Constrained
(1992), p. 34. feeds are classified as either series or parallel networks.
Feed blockage is the effect of shadowing of the main mirror A parallel feed is a type of constrained feed network in
in reflector antennas by a feed and feed-support structures. which paths to the individual elements proceed in parallel
Feed blockage introduces undesirable distortions in the from couplers or power splitters. The most common tech-
antenna pattern that can cause, for example, the broadening of nique for realizing a parallel feed structure is the matched
the main beam and rise in the sidelobe level. Typical effects corporate feed structure (Fig. F8), in which matched hybrids
of reflector blockage are shown in Fig. F7. Feed and feed- or used as power-dividing elements.
support blockage can be reduced by offsetting the reflector, A series feed is a type of constrained feed in which radi-
changing the metal support structures to dielectric ones, or ating elements are fed from couplers or power dividers
other special techniques. SAL arranged in series. The basic types of this configuration are
Ref.: Barton, (1988), pp. 158–160; Skolnik (1990), p. 6.35. the end-fed serial feed system, in which there is a transmis-