Page 189 - Radar Technology Encyclopedia
P. 189
179 feed, rotating feed, space (optical)
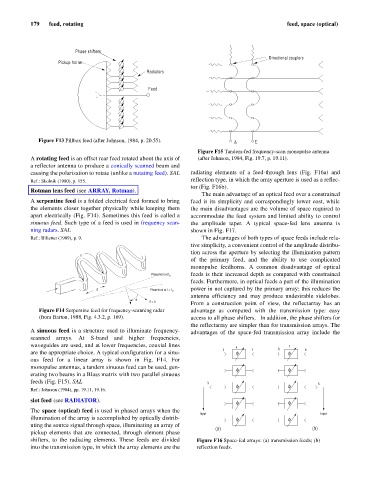
Phase shifters
Directional couplers
Pickup horns
Radiators
Feed
Figure F13 Pillbox feed (after Johnson, 1984, p. 20.55). D S
Figure F15 Tandem-fed frequency-scan monopulse antenna
A rotating feed is an offset rear feed rotated about the axis of (after Johnson, 1984, Fig. 19.7, p. 19.11).
a reflector antenna to produce a conically scanned beam and
causing the polarization to rotate (unlike a nutating feed). SAL radiating elements of a feed-through lens (Fig. F16a) and
Ref.: Skolnik (1980), p. 155. reflection type, in which the array aperture is used as a reflec-
tor (Fig. F16b).
Rotman lens feed (see ARRAY, Rotman).
The main advantage of an optical feed over a constrained
A serpentine feed is a folded electrical feed formed to bring feed is its simplicity and correspondingly lower cost, while
the elements closer together physically while keeping them the main disadvantages are the volume of space required to
apart electrically (Fig. F14). Sometimes this feed is called a accommodate the feed system and limited ability to control
sinuous feed. Such type of a feed is used in frequency scan- the amplitude taper. A typical space-fed lens antenna is
ning radars. SAL shown in Fig. F17.
Ref.: Billetter (1989), p. 9. The advantages of both types of space feeds include rela-
tive simplicity, a convenient control of the amplitude distribu-
tion across the aperture by selecting the illumination pattern
s
of the primary feed, and the ability to use complicated
monopulse feedhorns. A common disadvantage of optical
feeds is their increased depth as compared with constrained
Phasefront at f 0
feeds. Furthermore, in optical feeds a part of the illumination
d Phasefront at f < f 0 power in not captured by the primary array; this reduces the
antenna efficiency and may produce undesirable sidelobes.
q
q= 0
From a construction point of view, the reflectarray has an
Figure F14 Serpentine feed for frequency-scanning radar advantage as compared with the transmission type: easy
(from Barton, 1988, Fig. 4.3.2, p. 169). access to all phase shifters. In addition, the phase shifters for
the reflectarray are simpler than for transmission arrays. The
A sinuous feed is a structure used to illuminate frequency- advantages of the space-fed transmission array include the
scanned arrays. At S-band and higher frequencies,
waveguides are used, and at lower frequencies, coaxial lines 4 7
2 1 8 6
are the appropriate choice. A typical configuration for a sinu- f f
ous feed for a linear array is shown in Fig. F14. For
monopulse antennas, a tandem sinuous feed can be used, gen-
f f
erating two beams in a Blass matrix with two parallel sinuous
feeds (Fig. F15). SAL 3 5
f f
Ref.: Johnson (1984), pp. 19.11, 19.16.
slot feed (see RADIATOR). f f
The space (optical) feed is used in phased arrays when the
Input Input
illumination of the array is accomplished by optically distrib- f f
uting the source signal through space, illuminating an array of
(a) (b)
pickup elements that are connected, through element phase
shifters, to the radiating elements. These feeds are divided Figure F16 Space-fed arrays: (a) transmission feeds; (b)
into the transmission type, in which the array elements are the reflection feeds.