Page 204 - Radar Technology Encyclopedia
P. 204
filter, rippler filter, spatial 194
Along with smoothing of measurement data, ripple filters
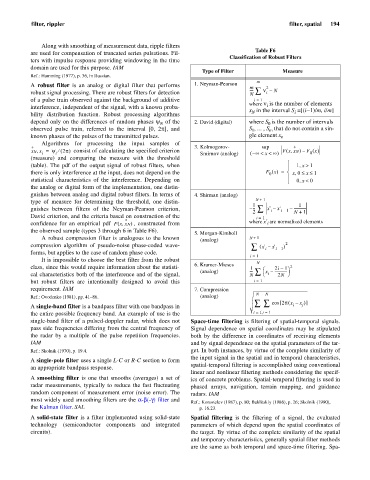
Table F6
are used for compensation of truncated series pulsations. Fil-
Classification of Robust Filters
ters with impulse response providing windowing in the time
domain are used for this purpose. IAM
Type of Filter Measure
Ref.: Hamming (1977), p. 36, in Russian.
m
A robust filter is an analog or digital filter that performs 1. Neyman-Pearson m 2
robust signal processing. There are robust filters for detection ---- å n – N
i
N
of a pulse train observed against the background of additive i = 1
where n is the number of elements
interference, independent of the signal, with a known proba- i
x in the interval S =[(i-1)/m, i/m]
N
i
bility distribution function. Robust processing algorithms
depend only on the differences of random phases y of the 2. David (digital) where S is the number of intervals
N
0
observed pulse train, referred to the interval [0, 2p], and S , ... , S that do not contain a sin-
m
1
known phases of the pulses of the transmitted pulses. gle element x n
Algorithms for processing the input samples of
3. Kolmogorov- sup
,
(
consist of calculating the specified criterion
xN x , = y 2p(¤ ) Fx xN ) F x ()
–
i i Smirnov (analog) – ( ¥ << ¥ ) 0
x
(measure) and comparing the measure with the threshold
(table). The pdf of the output signal of robust filters, when ì 1 x >, 1
ï
=
there is only interference at the input, does not depend on the F x () í x 0 ££, x 1
0
statistical characteristics of the interference. Depending on ï 0 x <, 0
î
the analog or digital form of the implementation, one distin-
guishes between analog and digital robust filters. In terms of 4. Shirman (analog)
N + 1
type of measure for determining the threshold, one distin- 1 1
guishes between filters of the Neyman-Pearson criterion, – --- å x' – x' i 1– – -------------
i
2 N + 1
David criterion, and the criteria based on construction of the i = 1
, constructed from
,
i
confidence for an empirical pdf Fx xN ) where x¢are normalized elements
(
the observed sample (types 3 through 6 in Table F6). 5. Morgan-Kimboll
A robust compression filter is analogous to the known (analog) N + 1
compression algorithm of pseudo-noise phase-coded wave- å ( x' – x' i 1– 2 )
i
forms, but applies to the case of random phase code.
i = 1
It is impossible to choose the best filter from the robust N
6. Kramer-Mieses
class, since this would require information about the statisti- 1 æ 2i – 1 ö
2
(analog) ---- å x – --------------
cal characteristics both of the interference and of the signal, N è i 2N ø
but robust filters are intentionally designed to avoid this i = 1
requirement. IAM 7. Compression
Ref.: Ovodenko (1981), pp. 41–86. (analog) N N
å å cos [ 2p x – x )]
(
A single-band filter is a bandpass filter with one bandpass in i j
the entire possible frequency band. An example of use is the i = 1 j = 1
single-band filter of a pulsed-doppler radar, which does not Space-time filtering is filtering of spatial-temporal signals.
pass side frequencies differing from the central frequency of Signal dependence on spatial coordinates may be stipulated
the radar by a multiple of the pulse repetition frequencies. both by the difference in coordinates of receiving elements
IAM and by signal dependence on the spatial parameters of the tar-
Ref.: Skolnik (1970), p. 19.4. get. In both instances, by virtue of the complete similarity of
the input signal in the spatial and in temporal characteristics,
A single-pole filter uses a single L-C or R-C section to form
spatial-temporal filtering is accomplished using conventional
an appropriate bandpass response.
linear and nonlinear filtering methods considering the specif-
A smoothing filter is one that smooths (averages) a set of ics of concrete problems. Spatial-temporal filtering is used in
radar measurements, typically to reduce the fast fluctuating phased arrays, navigation, terrain mapping, and guidance
random component of measurement error (noise error). The radars. IAM
most widely used smoothing filters are the a-b(-g) filter and
Ref.: Korostelev (1987), p. 80; Baklitskiy (1986), p. 26; Skolnik (1990),
the Kalman filter. SAL p. 16.23.
A solid-state filter is a filter implemented using solid-state Spatial filtering is the filtering of a signal, the evaluated
technology (semiconductor components and integrated parameters of which depend upon the spatial coordinates of
circuits). the target. By virtue of the complete similarity of the spatial
and temporary characteristics, generally spatial filter methods
are the same as both temporal and space-time filtering. Spa-