Page 237 - Radar Technology Encyclopedia
P. 237
227 jamming, count-down jamming, deception [deceptive]
Count-down jamming is jamming using an on–off type jam- (e.g., on the wingtips of the aircraft). Properly designed, this
ming signal with frequency and duty cycles to prevent the kind of jamming can be very effective against all types of
AGC of radar receiver from being at the right level. To tracking radars. Sometimes this technique is called two-point
increase the effectiveness, the jamming duty cycle is changed coherent jamming. (See also ECM, cross-eye). SAL
periodically (this fact is reflected in the name of the jamming, Ref.: Johnston (1979), p. 57; Barton (1989), p. 501; Schleher (1986), p. 158.
as originally a counter was used to perform a count-down to
Cross-polarization jamming is jamming based on the effect
determine the period of variation of the duty cycle). SAL
of cross-polarization and retransmitting a signal which is
Ref.: Neri (1991), p. 381.
polarized orthogonally to the polarization of the radar trans-
Cover-pulse jamming is a self-defense noise-jamming tech- mission. The cross-polarized signal, when received by a para-
nique in which the noise envelope is increased slowly from bolic or shaped reflector antenna, introduces large angle
zero at a time estimated to precede the arrival of the radar errors in tracking radars. (See also ECM, cross-polariza-
pulse at the target, forcing the radar CFAR threshold (or AGC tion). SAL
level) to increase enough to suppress the target echo. The Ref.: Barton (1991), p. 12.7; Leonov (1986), pp. 238–253.
level is decreased again to zero after arrival of the pulse.
Continuous-wave jamming is jamming using a CW carrier
When properly implemented, the radar operator may not rec-
waveform. It can be either unmodulated or modulated.
ognize that jamming has occurred, and no jam strobe is gener-
Unmodulated CW jamming is typically used against band-
ated. The duration of the cover pulse must be sufficient to
pass radars with limited tuning capability and employs the
counter the effects of variable pulse repetition interval, since
transmission of a high-power carrier frequency with the aim
initiation of the jamming is based on the time of arrival of the
of overloading the radar receiver. Modulated CW jamming is
previous pulse. DKB
a carrier waveform modulated with some other signals such
Ref.: Schleher (1986), p. 145.
as noise or signals with high, medium, or low frequencies,
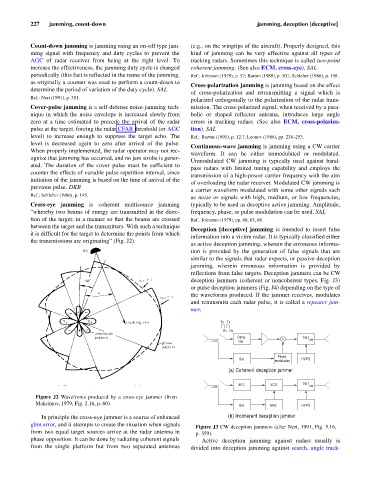
Cross-eye jamming is coherent multisource jamming typically to be used as deceptive active jamming. Amplitude,
“whereby two beams of energy are transmitted in the direc- frequency, phase, or pulse modulation can be used. SAL
tion of the target; in a manner so that the beams are crossed Ref.: Johnston (1979), pp. 60, 63, 68.
between the target and the transmitters. With such a technique
Deception [deceptive] jamming is intended to insert false
it is difficult for the target to determine the points from which
information into a victim radar. It is typically classified either
the transmissions are originating” (Fig. J2).
as active deception jamming, wherein the erroneous informa-
tion is provided by the generation of false signals that are
similar to the signals that radar expects, or passive deception
jamming, wherein erroneous information is provided by
reflections from false targets. Deception jammers can be CW
deception jammers (coherent or noncoherent types, Fig. J3)
or pulse deception jammers (Fig. J4) depending on the type of
the waveforms produced. If the jammer receives, modulates
and retransmits each radar pulse, it is called a repeater jam-
mer.
Tx Tx
Rx Rx
Delay TWT
line cw
Phase
Det. HVPS
modulation
(a) Coherent deception jammer
AFC VCO TWT cw
Figure J2 Wavefronts produced by a cross-eye jammer (from
Maksimov, 1979, Fig. 2.16, p. 60).
Det. Mod. HVPS
In principle the cross-eye jammer is a source of enhanced (b) Incoherent deception jammer
glint error, and it attempts to create the situation when signals
Figure J3 CW deception jammers (after Neri, 1991, Fig. 5.16,
from two equal target sources arrive at the radar antenna in p. 359).
phase opposition. It can be done by radiating coherent signals Active deception jamming against radars usually is
from the single platform but from two separated antennas divided into deception jamming against search, angle track-