Page 234 - Radar Technology Encyclopedia
P. 234
INTERPOLATION IONOSPHERE 224
The interpolation ratio is the ratio of the width of the
Table I3
radar resolution cell to the accuracy of the target position
Interrogator Mode Pulse Specifications
measurement in that coordinate. In angle this is also known as
the beam-splitting ratio. DKB
P1, P2, P3 Pulse duration: 0.8 ± 0.1 m s
Ref.: Barton (1988), p. 377.
pulses: Rise time: ³ 0.05 m s, £ 0.01m s
INTERROGATION, INTERROGATOR. Interrogation “in Decay time: ³ 0.05 m s, £ 0.02m s
a transponder system is the signal or combination of signals
intended tom trigger a response.” The interrogator is the Mode
transmitting part of a secondary surveillance radar (SSR). The spacing, P1–P2 Separation P1–P3 separation
Mode:
transmitter-receiver of such a system, properly called an
interrogator-responser, is sometimes referred to simply as an
±
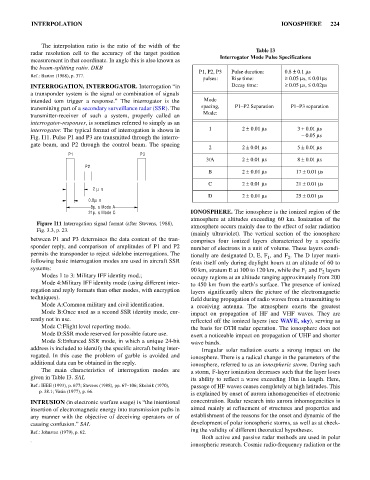
interrogator. The typical format of interrogation is shown in 1 2 0.01 m s 3 + 0.01 m s
Fig. I11. Pulse P1 and P3 are transmitted through the interro- - 0.05 m s
gate beam, and P2 through the control beam. The spacing
2 2 ± 0.01 m s 5 ± 0.01 m s
P1 P3
3/A 2 ± 0.01 m s 8 ± 0.01 m s
P2
±
B 2 0.01 m s 17 ± 0.01 m s
C 2 ± 0.01 m s 21 0.01 m s
±
m
2 s
±
D 2 0.01 m s 25 ± 0.01 m s
m
0.8 s
m
8 s Mode A
m
21 s Mode C IONOSPHERE. The ionosphere is the ionized region of the
atmosphere at altitudes exceeding 60 km. Ionization of the
Figure I11 Interrogation signal format (after Stevens, 1988),
atmosphere occurs mainly due to the effect of solar radiation
Fig. 3.3, p. 23.
(mainly ultraviolet). The vertical section of the ionosphere
between P1 and P3 determines the data content of the tran- comprises four ionized layers characterized by a specific
sponder reply, and comparison of amplitudes of P1 and P2 number of electrons in a unit of volume. These layers condi-
permits the transponder to reject sidelobe interrogations. The tionally are designated D, E, F , and F . The D layer mani-
2
1
following basic interrogation modes are used in aircraft SSR fests itself only during daylight hours at an altitude of 60 to
systems: 90 km, stratum E at 100 to 120 km, while the F and F layers
1
2
Modes 1 to 3: Military IFF identity mod.; occupy regions at an altitude ranging approximately from 200
Mode 4:Military IFF identity mode (using different inter- to 450 km from the earth’s surface. The presence of ionized
rogation and reply formats than other modes, with encryption layers significantly alters the picture of the electromagnetic
techniques). field during propagation of radio waves from a transmitting to
Mode A:Common military and civil identification. a receiving antenna. The atmosphere exerts the greatest
Mode B:Once used as a second SSR identity mode, cur- impact on propagation of HF and VHF waves. They are
rently not in use. reflected off the ionized layers (see WAVE, sky), serving as
Mode C:Flight level reporting mode. the basis for OTH radar operation. The ionosphere does not
Mode D:SSR mode reserved for possible future use. exert a noticeable impact on propagation of UHF and shorter
Mode S:Enhanced SSR mode, in which a unique 24-bit wave bands.
address is included to identify the specific aircraft being inter- Irregular solar radiation exerts a strong impact on the
rogated. In this case the problem of garble is avoided and ionosphere. There is a radical change in the parameters of the
additional data can be obtained in the reply. ionosphere, referred to as an ionospheric storm. During such
The main characteristics of interrogation modes are a storm, F-layer ionization decreases such that the layer loses
given in Table I3. SAL its ability to reflect a wave exceeding 10m in length. Here,
Ref.: IEEE (1993), p. 677; Stevens (1988), pp. 67–106; Skolnik (1970), passage of HF waves ceases completely at high latitudes. This
p. 38.1; Vasin (1977), p. 66.
is explained by onset of aurora inhomogeneities of electronic
INTRUSION (in electronic warfare usage) is “the intentional concentration. Radar research into aurora inhomogeneities is
insertion of electromagnetic energy into transmission paths in aimed mainly at refinement of structures and properties and
any manner with the objective of deceiving operators or of establishment of the reasons for the onset and dynamic of the
causing confusion.” SAL development of polar ionospheric storms, as well as at check-
ing the validity of different theoretical hypotheses.
Ref.: Johnston (1979), p. 62.
Both active and passive radar methods are used in polar
.
ionospheric research. Cosmic radio-frequency radiation or the