Page 238 - Radar Technology Encyclopedia
P. 238
jamming, deception [deceptive] jamming, ground-bounce 228
False target jamming is jamming that transmits replicas of
the radar pulses so the received pulses appear to be targets. If
TWT
Mod. cw
the replicas are received through the antenna sidelobes, the
angular location of the false target appears to be very different
from that of the jamming source and many different targets
DL HVPS
can be created with different angular locations. The main
methods to reduce the effectiveness of false target jamming
Warning Deception are to use waveforms that are rather difficult to repeat or to
logic program
use an auxiliary antenna and compare the energies received to
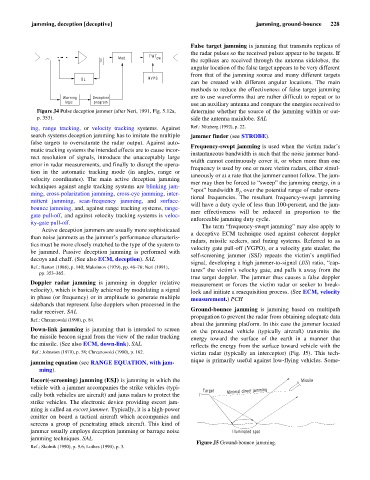
Figure J4 Pulse deception jammer (after Neri, 1991, Fig. 5.12a, determine whether the source of the jamming within or out-
p. 353). side the antenna mainlobe. SAL
ing, range tracking, or velocity tracking systems. Against Ref.: Nitzberg (1992), p. 22.
search systems deception jamming has to imitate the multiple jammer finder (see STROBE).
false targets to oversaturate the radar output. Against auto-
Frequency-swept jamming is used when the victim radar’s
matic tracking systems the intended effects are to cause incor-
instantaneous bandwidth is such that the noise jammer band-
rect resolution of signals, introduce the unacceptably large
width cannot continuously cover it, or when more than one
error in radar measurements, and finally to disrupt the opera-
frequency is used by one or more victim radars, either simul-
tion in the automatic tracking mode (in angles, range or
taneously or at a rate that the jammer cannot follow. The jam-
velocity coordinates). The main active deception jamming
mer may then be forced to “sweep” the jamming energy, in a
techniques against angle tracking systems are blinking jam-
“spot” bandwidth B , over the potential range of radar opera-
j
ming, cross-polarization jamming, cross-eye jamming, inter-
tional frequencies. The resultant frequency-swept jamming
mittent jamming, scan-frequency jamming, and surface-
will have a duty cycle of less than 100-percent, and the jam-
bounce jamming, and, against range tracking systems, range-
mer effectiveness will be reduced in proportion to the
gate pull-off, and against velocity tracking systems is veloc-
enforceable jamming duty cycle.
ity-gate pull-off.
The term “frequency-swept jamming” may also apply to
Active deception jammers are usually more sophisticated
a deceptive ECM technique used against coherent doppler
than noise jammers as the jammer’s performance characteris-
radars, missile seekers, and fuzing systems. Referred to as
tics must be more closely matched to the type of the system to
velocity gate pull-off (VGPO), or a velocity gate stealer, the
be jammed. Passive deception jamming is performed with
self-screening jammer (SSJ) repeats the victim’s amplified
decoys and chaff. (See also ECM, deception). SAL
signal, developing a high jammer-to-signal (J/S) ratio, “cap-
Ref.: Barton (1988), p. 140; Maksimov (1979), pp. 46–76; Neri (1991),
tures” the victim’s velocity gate, and pulls it away from the
pp. 353–365.
true target doppler. The jammer thus causes a false doppler
Doppler radar jamming is jamming in doppler (relative
measurement or forces the victim radar or seeker to break-
velocity), which is basically achieved by modulating a signal
lock and initiate a reacquisition process. (See ECM, velocity
in phase (or frequency) or in amplitude to generate multiple
measurement.) PCH
sidebands that represent false dopplers when processed in the
Ground-bounce jamming is jamming based on multipath
radar receiver. SAL
propagation to prevent the radar from obtaining adequate data
Ref.: Chrzanowski (1990), p. 84.
about the jamming platform. In this case the jammer located
Down-link jamming is jamming that is intended to screen
on the protected vehicle (typically aircraft) transmits the
the missile beacon signal from the view of the radar tracking
energy toward the surface of the earth in a manner that
the missile. (See also ECM, down-link). SAL
reflects the energy from the surface toward vehicle with the
Ref.: Johnston (1979), p. 58; Chrzanowski (1990), p. 162. victim radar (typically an interceptor) (Fig. J5). This tech-
nique is primarily useful against low-flying vehicles. Some-
jamming equation (see RANGE EQUATION, with jam-
ming).
Escort(-screening) jamming (ESJ) is jamming in which the Missile
vehicle with a jammer accompanies the strike vehicles (typi-
Target Minimal direct jamming
cally both vehicles are aircraft) and jams radars to protect the
strike vehicles. The electronic device providing escort jam-
ming is called an escort jammer. Typically, it is a high-power
emitter on board a tactical aircraft which accompanies and
screens a group of penetrating attack aircraft. This kind of
jammer usually employs deception jamming or barrage noise Illuminated spot
jamming techniques. SAL
Figure J5 Ground-bounce jamming.
Ref.: Skolnik (1990), p. 9.6; Lothes (1990), p. 3.