Page 280 - Radar Technology Encyclopedia
P. 280
modulation, amplitude modulation, frequency 270
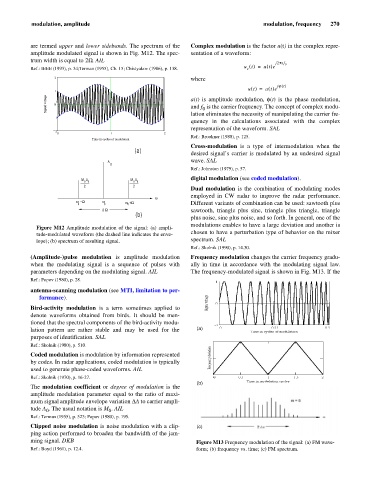
are termed upper and lower sidebands. The spectrum of the Complex modulation is the factor u(t) in the complex repre-
amplitude modulated signal is shown in Fig. M12. The spec- sentation of a waveform:
trum width is equal to 2W. AIL
j2ptf 0
=
Ref.: IEEE (1993), p. 34;Terman (1955), Ch. 15; Chistyakov (1986), p. 138. u t () ut () e
c
2 where
jj t ()
=
ut () at () e
1
Signal voltage 0 a(t) is amplitude modulation, f(t) is the phase modulation,
and f is the carrier frequency. The concept of complex modu-
0
lation eliminates the necessity of manipulating the carrier fre-
1
quency in the calculations associated with the complex
representation of the waveform. SAL
2
0 1 2
Ref.: Brookner (1988), p. 125.
Time in cycles of modulation
Cross-modulation is a type of intermodulation when the
(a)
desired signal’s carrier is modulated by an undesired signal
A wave. SAL
0
Ref.: Johnston (1979), p. 57.
digital modulation (see coded modulation).
M A M A
0 0 0 0
2 2
Dual modulation is the combination of modulating modes
employed in CW radar to improve the radar performance.
w
w -W w w +W
0 0 0 Different variants of combination can be used: sawtooth plus
2 W sawtooth, triangle plus sine, triangle plus triangle, triangle
(b)
plus noise, sine plus noise, and so forth. In general, one of the
modulations enables to have a large deviation and another is
Figure M12 Amplitude modulation of the signal: (a) ampli-
tude-modulated waveform (the dashed line indicates the enve- chosen to have a perturbation type of behavior on the mixer
lope); (b) spectrum of resulting signal. spectrum. SAL
Ref.: Skolnik (1990), p. 14.30.
(Amplitude-)pulse modulation is amplitude modulation Frequency modulation changes the carrier frequency gradu-
when the modulating signal is a sequence of pulses with ally in time in accordance with the modulating signal law.
parameters depending on the modulating signal. AIL The frequency-modulated signal is shown in Fig. M13. If the
Ref.: Popov (1980), p. 28.
antenna-scanning modulation (see MTI, limitation to per-
formance).
Bird-activity modulation is a term sometimes applied to
denote waveforms obtained from birds. It should be men-
tioned that the spectral components of the bird-activity modu-
lation pattern are rather stable and may be used for the (a)
purposes of identification. SAL
Ref.: Skolnik (1980), p. 510.
Coded modulation is modulation by information represented
by codes. In radar applications, coded modulation is typically
used to generate phase-coded waveforms. AIL
Ref.: Skolnik (1970), p. 16-27.
(b)
The modulation coefficient or degree of modulation is the
amplitude modulation parameter equal to the ratio of maxi-
mum signal amplitude envelope variation DA to carrier ampli-
tude A . The usual notation is M . AIL
0
0
Ref.: Terman (1955), p. 523; Popov (1980), p. 195.
Clipped noise modulation is noise modulation with a clip- (c)
ping action performed to broaden the bandwidth of the jam-
ming signal. DKB Figure M13 Frequency modulation of the signal: (a) FM wave-
Ref.: Boyd (1961), p. 12.4. form; (b) frequency vs. time; (c) FM spectrum.