Page 36 - Radiochemistry and nuclear chemistry
P. 36
Nuclei, Isotopes and Isotope Separation 25
F = ftr frot fvib = (2"x~T/h3)3/2VMaTr21r kTe-U/2/{h2ks(1 -e-u)} (2.34)
where k s is a symmetry constant for rotation and u = hcxo/kT. This expression holds for
all molecules in (2.15). Thus for the ratio one gets
FAx~FAx* = (M* /Mr)3/2ksIr* (1 -e-U)e-U*/2/ {ks*lr(1 _e-u*)e -u/2} (2.35)
where the asterisk refers to molecule AX*. This relation shows the mass dependency of the
equilibrium constant (2.16) (a similar relation holds for the BX-BX* combination). (2.35)
contains factors all of which can be determined spectroscopically. Consequently, the
equilibrium constants for isotope exchange reactions can be, and have been, calculated for
many systems.
2.6.5. Paleotemperatures and other applications
Eqn (2.35) contains the temperature in the exponent. Isotope exchange equilibria are thus
temperature dependent. A practical use of this fact is the determination of
paleotemperatures. In the isotope exchange reaction
C 1602(g ) + H2180(1) = C 180 160(g) + H2160(1)
the oxygen isotopes in CO 2 exchange with the oxygen isotopes in H20. The value of the
equilibrium constant (mole fractions) k - 1.046 (0~ indicates that 180 will be slightly
enriched in the CO 2 by the reaction. Thus if carbon dioxide is bubbled through water, the
emergent gas will be more enriched in the 18 O than the residual water. In this reaction, the
isotope effect is said to be 4.6 %. The following reaction occurs with carbonate ions in
water:
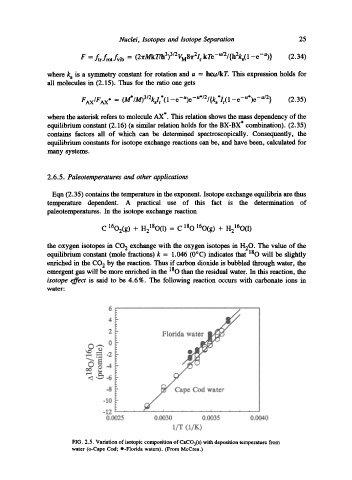
FIG. 2.5. Variation of isotopic composition of CaCO3(s) with deposition temperature from
water (o-Cape Cod; O-Florida waters). (From McCrea.)