Page 32 - Rapid Learning in Robotics
P. 32
18 The Robotics Laboratory
cessor board. Following the example of RCCL, the “Manus Control C
Library” (MCCL) was developed and implemented (Rankers 1994; Selle
1995). To facilitate an arm-hand unified planning level, the Unix work-
station “druide” is set up to issue finger motion (piston, joint, or Cartesian
position) and force control requests to the “manus” controller (Fig. 2.2).
X
Oil System Finger f
F e τ DC Motor
f, des PD Cylinder
- K -1 + and
Controller + F
Oil Cylinder ext
Environment
X f, des
-
X
m p F
friction
X f, estim Oil Model
F f, estim Finger Further
State Fingertip
Estimation Sensors
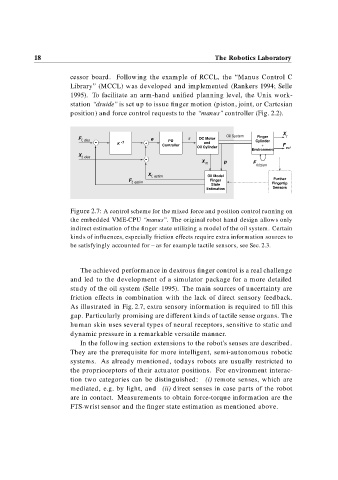
Figure 2.7: A control scheme for the mixed force and position control running on
the embedded VME-CPU “manus”. The original robot hand design allows only
indirect estimation of the finger state utilizing a model of the oil system. Certain
kinds of influences, especially friction effects require extra information sources to
be satisfyingly accounted for – as for example tactile sensors, see Sec. 2.3.
The achieved performance in dextrous finger control is a real challenge
and led to the development of a simulator package for a more detailed
study of the oil system (Selle 1995). The main sources of uncertainty are
friction effects in combination with the lack of direct sensory feedback.
As illustrated in Fig. 2.7, extra sensory information is required to fill this
gap. Particularly promising are different kinds of tactile sense organs. The
human skin uses several types of neural receptors, sensitive to static and
dynamic pressure in a remarkable versatile manner.
In the following section extensions to the robot's senses are described.
They are the prerequisite for more intelligent, semi-autonomous robotic
systems. As already mentioned, todays robots are usually restricted to
the proprioceptors of their actuator positions. For environment interac-
tion two categories can be distinguished: (i) remote senses, which are
mediated, e.g. by light, and (ii) direct senses in case parts of the robot
are in contact. Measurements to obtain force-torque information are the
FTS-wrist sensor and the finger state estimation as mentioned above.