Page 166 - Rashid, Power Electronics Handbook
P. 166
10 Diode Recti®ers 155
given by
dIðDRÞ N S 1
¼ V IN ÿ V o ð10:84Þ
dt N P L 1
where V is the dc output voltage of the converter.
o
The ¯ywheel diode D is reversely biased by Vð9Þ, the
F
voltage at node 9
Vð9Þ¼ V ðN =N Þ for 0 < t < DT ð10:85Þ
IN S p
The magnetic-reset clamping diode D M is reversely
biased by the negative voltage at node 100. Assuming
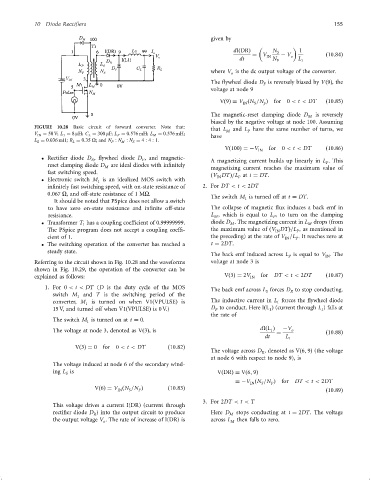
FIGURE 10.28 Basic circuit of forward converter. Note that: that L and L have the same number of turns, we
V IN ¼ 50 V; L 1 ¼ 8 mH; C L ¼ 300 mF; L P ¼ 0:576 mH; L M ¼ 0:576 mH; M P
have
L S ¼ 0:036 mH; R L ¼ 0:35 O; and N P : N M : N S ¼ 4 : 4 : 1.
Vð100Þ¼ ÿV for 0 < t < DT ð10:86Þ
IN
Recti®er diode D , ¯ywheel diode D , and magnetic- A magnetizing current builds up linearly in L . This
F
R
reset clamping diode D are ideal diodes with in®nitely P
M magnetizing current reaches the maximum value of
fast switching speed.
ðV DTÞ=L at t ¼ DT.
P
IN
Electronic switch M is an idealized MOS switch with
1
in®nitely fast switching speed, with on-state resistance of 2. For DT < t < 2DT
0:067 O, and off-state resistance of 1 MO.
The switch M is turned off at t ¼ DT.
1
It should be noted that PSpice does not allow a switch
to have zero on-state resistance and in®nite off-state The collapse of magnetic ¯ux induces a back emf in
resistance. L , which is equal to L , to turn on the clamping
M
P
Transformer T has a coupling coef®cient of 0.99999999. diode D . The magnetizing current in L drops (from
M
M
1
The PSpice program does not accept a coupling coef®- the maximum value of ðV DTÞ=L , as mentioned in
IN
P
cient of 1. the preceding) at the rate of V =L . It reaches zero at
IN
P
The switching operation of the converter has reached a t ¼ 2DT.
steady state.
The back emf induced across L is equal to V . The
IN
P
Referring to the circuit shown in Fig. 10.28 and the waveforms voltage at node 3 is
shown in Fig. 10.29, the operation of the converter can be
explained as follows: Vð3Þ¼ 2V IN for DT < t < 2DT ð10:87Þ
1. For 0 < t < DT (D is the duty cycle of the MOS The back emf across L forces D to stop conducting.
R
S
switch M 1 and T is the switching period of the
converter, M 1 is turned on when V1ðVPULSEÞ is The inductive current in L forces the ¯ywheel diode
1
15 V, and turned off when V1ðVPULSEÞ is 0 V.) D to conduct. Here IðL Þ (current through L ) falls at
F
1
1
the rate of
The switch M is turned on at t ¼ 0.
1
The voltage at node 3, denoted as Vð3Þ,is dIðL Þ ¼ ÿV o ð10:88Þ
1
dt L
1
Vð3Þ¼ 0 for 0 < t < DT ð10:82Þ
The voltage across D , denoted as Vð6; 9Þ (the voltage
R
at node 6 with respect to node 9), is
The voltage induced at node 6 of the secondary wind-
ing L is VðDRÞ¼ Vð6; 9Þ
S
¼ÿV ðN =N Þ for DT < t < 2DT
IN
S
P
Vð6Þ¼ V ðN =N Þ ð10:83Þ ð10:89Þ
P
S
IN
3. For 2DT < t < T
This voltage drives a current I(DR) (current through
recti®er diode D ) into the output circuit to produce Here D M stops conducting at t ¼ 2DT. The voltage
R
the output voltage V . The rate of increase of I(DR) is across L M then falls to zero.
o