Page 375 - Refining Biomass Residues for Sustainable Energy and Bioproducts
P. 375
Bioenergy generation from agricultural wastes and enrichment of end products 339
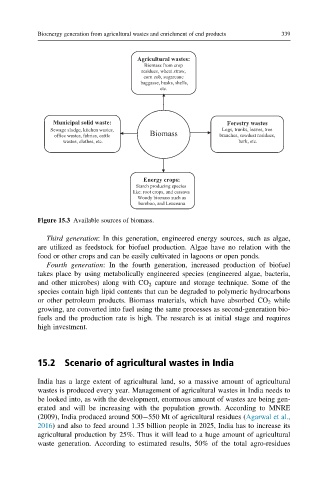
Agricultural wastes:
Biomass from crop
residues, wheat straw,
corn cob, sugarcane
baggasse, husks, shells,
etc.
Municipal solid waste: Forestry wastes
Sewage sludge, kitchen wastes, Logs, trunks, leaves, tree
office wastes, fabrics, cattle Biomass branches, sawdust residues,
wastes, clothes, etc. bark, etc.
Energy crops:
Starch producing species
like: root crops, and cassava
Woody biomass such as
bamboo, and Leuceana
Figure 15.3 Available sources of biomass.
Third generation: In this generation, engineered energy sources, such as algae,
are utilized as feedstock for biofuel production. Algae have no relation with the
food or other crops and can be easily cultivated in lagoons or open ponds.
Fourth generation: In the fourth generation, increased production of biofuel
takes place by using metabolically engineered species (engineered algae, bacteria,
and other microbes) along with CO 2 capture and storage technique. Some of the
species contain high lipid contents that can be degraded to polymeric hydrocarbons
or other petroleum products. Biomass materials, which have absorbed CO 2 while
growing, are converted into fuel using the same processes as second-generation bio-
fuels and the production rate is high. The research is at initial stage and requires
high investment.
15.2 Scenario of agricultural wastes in India
India has a large extent of agricultural land, so a massive amount of agricultural
wastes is produced every year. Management of agricultural wastes in India needs to
be looked into, as with the development, enormous amount of wastes are being gen-
erated and will be increasing with the population growth. According to MNRE
(2009), India produced around 500 550 Mt of agricultural residues (Agarwal et al.,
2016) and also to feed around 1.35 billion people in 2025, India has to increase its
agricultural production by 25%. Thus it will lead to a huge amount of agricultural
waste generation. According to estimated results, 50% of the total agro-residues