Page 74 - Robots Androids and Animatrons : 12 Incredible Projects You Can Build
P. 74
2.2K Vcc 10K
8 4 84
7 10K
To
150 Trigger To Servo Motor
555 Output 555
2 3 6 3
6 7 Trigger Vcc
10 1 Waveform .1 F 5 1 2 Servo
F .01 Waveform Motor
F
Approx 55 HZ 1-2 ms
18 ms
18 ms
1 ms
Astable Monostable
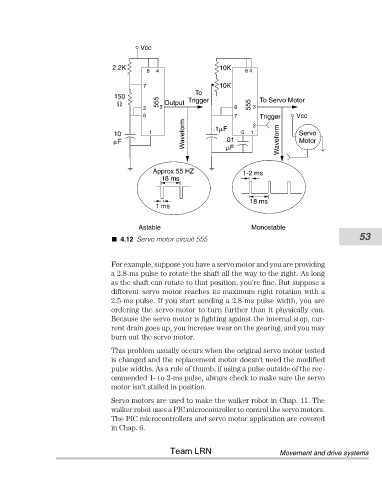
4.12 Servo motor circuit 555 53
For example, suppose you have a servo motor and you are providing
a 2.8-ms pulse to rotate the shaft all the way to the right. As long
as the shaft can rotate to that position, you’re fine. But suppose a
different servo motor reaches its maximum right rotation with a
2.5-ms pulse. If you start sending a 2.8-ms pulse width, you are
ordering the servo motor to turn further than it physically can.
Because the servo motor is fighting against the internal stop, cur-
rent drain goes up, you increase wear on the gearing, and you may
burn out the servo motor.
This problem usually occurs when the original servo motor tested
is changed and the replacement motor doesn’t need the modified
pulse widths. As a rule of thumb, if using a pulse outside of the rec-
ommended 1- to 2-ms pulse, always check to make sure the servo
motor isn’t stalled in position.
Servo motors are used to make the walker robot in Chap. 11. The
walker robot uses a PIC microcontroller to control the servo motors.
The PIC microcontrollers and servo motor application are covered
in Chap. 6.
Team LRN Movement and drive systems