Page 358 - Rock Mechanics For Underground Mining
P. 358
ROCK SUPPORT AND REINFORCEMENT
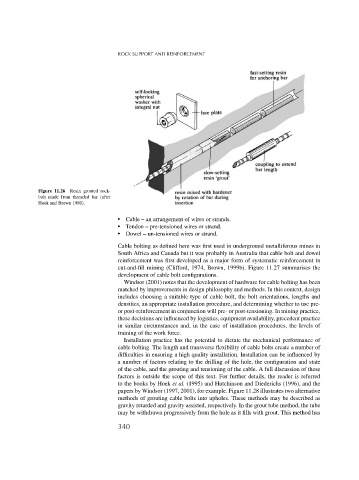
Figure 11.26 Resin grouted rock-
bolt made from threaded bar (after
Hoek and Brown 1980).
Cable – an arrangement of wires or strands.
Tendon – pre-tensioned wires or strand.
Dowel – un-tensioned wires or strand.
Cable bolting as defined here was first used in underground metalliferous mines in
South Africa and Canada but it was probably in Australia that cable bolt and dowel
reinforcement was first developed as a major form of systematic reinforcement in
cut-and-fill mining (Clifford, 1974, Brown, 1999b). Figure 11.27 summarises the
development of cable bolt configurations.
Windsor (2001) notes that the development of hardware for cable bolting has been
matched by improvements in design philosophy and methods. In this context, design
includes choosing a suitable type of cable bolt, the bolt orientations, lengths and
densities, an appropriate installation procedure, and determining whether to use pre-
or post-reinforcement in conjunction will pre- or post-tensioning. In mining practice,
these decisions are influenced by logistics, equipment availability, precedent practice
in similar circumstances and, in the case of installation procedures, the levels of
training of the work force.
Installation practice has the potential to dictate the mechanical performance of
cable bolting. The length and transverse flexibility of cable bolts create a number of
difficulties in ensuring a high quality installation. Installation can be influenced by
a number of factors relating to the drilling of the hole, the configuration and state
of the cable, and the grouting and tensioning of the cable. A full discussion of these
factors is outside the scope of this text. For further details, the reader is referred
to the books by Hoek et al. (1995) and Hutchinson and Diederichs (1996), and the
papers by Windsor (1997, 2001), for example. Figure 11.28 illustrates two alternative
methods of grouting cable bolts into upholes. These methods may be described as
gravity retarded and gravity assisted, respectively. In the grout tube method, the tube
may be withdrawn progressively from the hole as it fills with grout. This method has
340