Page 570 - Rock Mechanics For Underground Mining
P. 570
MONITORING ROCK MASS PERFORMANCE
Figure 18.5 Self-inductance
multiple-point borehole extensometer
(after Londe, 1982).
18.2.5 Hydraulic pressure cells
Hydraulic pressure cells are used to measure changes in total normal stress in materials
such as fill, shotcrete or concrete, or at interfaces between materials such as rock
and shotcrete or rock and concrete. The original form of hydraulic pressure cell
described by Brady and Brown (1985) consisted of a flatjack connected to a hydraulic
or pneumatic diaphragm transducer which was in turn connected by flexible tubing to
a read-out unit. Normal stress transferred from the surrounding soil, rock, shotcrete
or concrete was measured by balancing the fluid pressure applied to the reverse side
of the diaphragm. Procedures for monitoring normal stresses with hydraulic pressure
cells of this type are given by Franklin (1977) and the International Society for Rock
Mechanics Commission on Standardization of Laboratory and Field Tests (1980).
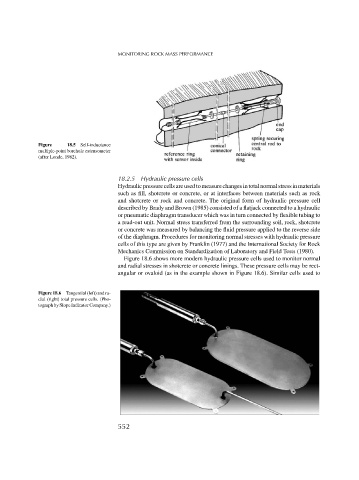
Figure 18.6 shows more modern hydraulic pressure cells used to monitor normal
and radial stresses in shotcrete or concrete linings. These pressure cells may be rect-
angular or ovaloid (as in the example shown in Figure 18.6). Similar cells used to
Figure 18.6 Tangential (left) and ra-
dial (right) total pressure cells. (Pho-
tograph by Slope Indicator Company.)
552