Page 224 - Root Cause Failure Analysis
P. 224
212 Root Cause Failure Analysis
IN IN
$. $.
$. CLOSED
WT
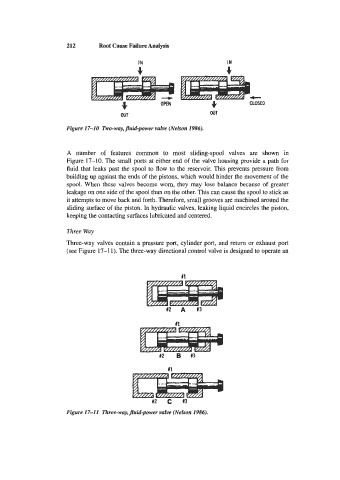
Figure 17-10 Two-way, fluid-power valve (Nelson 1986).
A number of features common to most sliding-spool valves are shown in
Figure 17-10. The small ports at either end of the valve housing provide a path for
fluid that leaks past the spool to flow to the reservoir. This prevents pressure from
building up against the ends of the pistons, which would hinder the movement of the
spool. When these valves become worn, they may lose balance because of greater
leakage on one side of the spool than on the other. This can cause the spool to stick as
it attempts to move back and forth. Therefore, small grooves are machined around the
sliding surface of the piston. In hydraulic valves, leaking liquid encircles the piston,
keeping the contacting surfaces lubricated and centered.
Three Way
Three-way valves contain a pressure port, cylinder port, and return or exhaust port
(see Figure 17-1 1). The three-way directional control valve is designed to operate an
I1
12 B Y3
il
Figure 17-11 Three-way, fluid-power valve (Nelson 1986).