Page 127 - Rotating Machinery Pratical Solutions to Unbalance and Misalignment
P. 127
Advanced Machine Alignment
ing the minimum torque value of the grade 5. If the grade 2 fas-
tener were torqued to its maximum, it would produce a clamping
force of only 67% of the minimum clamping force of the grade 5
fastener.
Most often, fastener manufacturers state the recommended
torque value for clean, dry threads. Any lubricant or debris on the
threads will greatly effect the torque value.
A very small amount of oil on the threads will reduce the
friction significantly—enough to reduce the recommended torque
by about 15% to 25%. Some of the newer Teflon- or Molybdenum-
based dry type lubricants can reduce the torque required by as
much as 50%. Often, zinc-plated fasteners can be found in indus-
trial applications. This plating will reduce the amount of required
torque by 15%.
Table 8-2 illustrates the tensile strength for various grades of
fasteners.
Table 8-2. Properties of Various Grade Fasteners
————————————————————————————————
TENSILE
GRADE MATERIAL STRENGTH (psi)
————————————————————————————————
2 Low carbon 74,000
5 Medium - carbon, tempered 120,000
8 Medium - carbon, tempered & quenched 150,000
————————————————————————————————
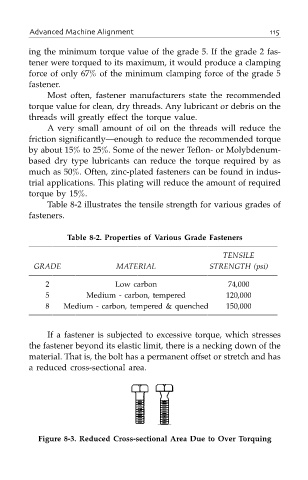
If a fastener is subjected to excessive torque, which stresses
the fastener beyond its elastic limit, there is a necking down of the
material. That is, the bolt has a permanent offset or stretch and has
a reduced cross-sectional area.
Figure 8-3. Reduced Cross-sectional Area Due to Over Torquing