Page 155 - Science at the nanoscale
P. 155
RPS: PSP0007 - Science-at-Nanoscale
10:15
June 5, 2009
7.1. Some Basic Thermodynamic Definitions
6
G
G
G
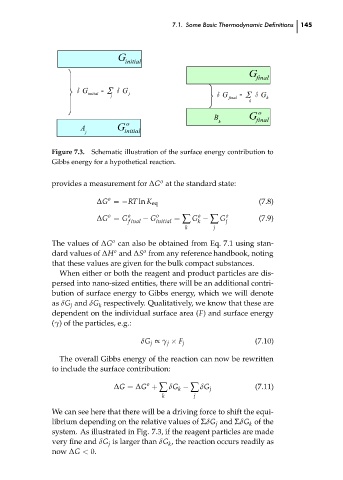
Schematic illustration of the surface energy contribution to
Figure 7.3.
Gibbs energy for a hypothetical reaction.
o
provides a measurement for ∆G at the standard state:
o
(7.8)
∆G = −RT ln K eq
o
o
o
o
∆G = G
− G
(7.9)
k ∑
=
initial
f inal
k
o
The values of ∆G can also be obtained from Eq. 7.1 using stan-
o
o
dard values of ∆H and ∆S from any reference handbook, noting
that these values are given for the bulk compact substances.
When either or both the reagent and product particles are dis-
persed into nano-sized entities, there will be an additional contri-
bution of surface energy to Gibbs energy, which we will denote
as δG and δG respectively. Qualitatively, we know that these are
k
j
dependent on the individual surface area (F) and surface energy
(γ) of the particles, e.g.:
δG j ∝ γ j × F j ∑ G − j G G o j 6 (7.10) 145 ch07
The overall Gibbs energy of the reaction can now be rewritten
to include the surface contribution:
o
k ∑
∆G = ∆G + ∑ δG − δG j (7.11)
k j
We can see here that there will be a driving force to shift the equi-
librium depending on the relative values of ΣδG j and ΣδG of the
k
system. As illustrated in Fig. 7.3, if the reagent particles are made
very fine and δG is larger than δG , the reaction occurs readily as
j
k
now ∆G < 0.