Page 155 - Sedimentology and Stratigraphy
P. 155
142 Rivers and Alluvial Fans
relatively steep depositional surface and there is a
distinct break in slope at the fan toe, the limit of the
deposition of coarse detritus at the edge of the alluvial
fan. The fan deposits are thickest at the apex and
taper as a conical wedge towards the toe.
Fig. 9.18 Alluvial fans in the Death Valley, USA, a region
with a hot, arid climate.
'((
Fig. 9.19 A colluvial fan, a mixture of scree and debris
flows in a cold, relatively dry setting in the Arctic. ' '(
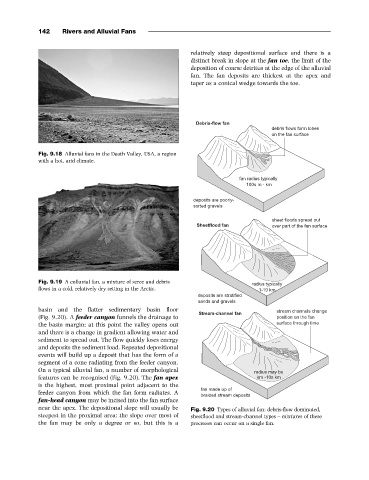
basin and the flatter sedimentary basin floor
(Fig. 9.20). A feeder canyon funnels the drainage to
the basin margin: at this point the valley opens out
and there is a change in gradient allowing water and
sediment to spread out. The flow quickly loses energy
and deposits the sediment load. Repeated depositional
events will build up a deposit that has the form of a
segment of a cone radiating from the feeder canyon.
On a typical alluvial fan, a number of morphological
features can be recognised (Fig. 9.20). The fan apex '(
is the highest, most proximal point adjacent to the
feeder canyon from which the fan form radiates. A
fan-head canyon may be incised into the fan surface
near the apex. The depositional slope will usually be Fig. 9.20 Types of alluvial fan: debris-flow dominated,
steepest in the proximal area: the slope over most of sheetflood and stream-channel types – mixtures of these
the fan may be only a degree or so, but this is a processes can occur on a single fan.