Page 129 - Semiconductor Manufacturing Handbook
P. 129
Geng(SMH)_CH10.qxd 04/04/2005 19:46 Page 10.2
ION IMPLANTATION AND RAPID THERMAL PROCESSING
10.2 WAFER PROCESSING
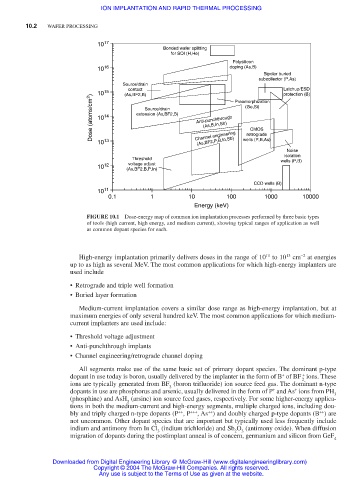
10 17
Bonded wafer splitting
for SOI (H,He)
Polysilicon
10 16 doping (As,B)
Bipolar buried
subcollector (P,As)
Source/drain
contact Latchup/ESD
10 15 (As,BF2,B) Preamorphization protection (B)
Dose (atoms/cm 2 ) 10 14 extension (As,BF2,B) Anti-punchthrough (Ge,Si)
Source/drain
(As,B,In,Sb)
CMOS
retrograde
(As,BF2,P,B,In,Sb)
10 13 Channel engineering wells (P,B,As)
Noise
isolation
Threshold wells (P,B)
10 12 voltage adjust
(As,BF2,B,P,In)
CCD wells (B)
10 11
0.1 1 10 100 1000 10000
Energy (keV)
FIGURE 10.1 Dose-energy map of common ion implantation processes performed by three basic types
of tools (high current, high energy, and medium current), showing typical ranges of application as well
as common dopant species for each.
High-energy implantation primarily delivers doses in the range of 10 to 10 cm at energies
11
13
−2
up to as high as several MeV. The most common applications for which high-energy implanters are
used include
• Retrograde and triple well formation
• Buried layer formation
Medium-current implantation covers a similar dose range as high-energy implantation, but at
maximum energies of only several hundred keV. The most common applications for which medium-
current implanters are used include:
• Threshold voltage adjustment
• Anti-punchthrough implants
• Channel engineering/retrograde channel doping
All segments make use of the same basic set of primary dopant species. The dominant p-type
+
+
dopant in use today is boron, usually delivered by the implanter in the form of B of BF ions. These
2
ions are typically generated from BF (boron trifluoride) ion source feed gas. The dominant n-type
3
+
+
dopants in use are phosphorus and arsenic, usually delivered in the form of P and As ions from PH 3
(phosphine) and AsH (arsine) ion source feed gases, respectively. For some higher-energy applica-
3
tions in both the medium-current and high-energy segments, multiple charged ions, including dou-
++
++
++
bly and triply charged n-type dopants (P , P +++ , As ) and doubly charged p-type dopants (B ) are
not uncommon. Other dopant species that are important but typically used less frequently include
indium and antimony from In Cl (indium trichloride) and Sb O (antimony oxide). When diffusion
3
3
2
migration of dopants during the postimplant anneal is of concern, germanium and silicon from GeF
4
Downloaded from Digital Engineering Library @ McGraw-Hill (www.digitalengineeringlibrary.com)
Copyright © 2004 The McGraw-Hill Companies. All rights reserved.
Any use is subject to the Terms of Use as given at the website.