Page 555 - Sensors and Control Systems in Manufacturing
P. 555
508
T e n
Cha p te r
For an MPD of 0.122 cm, the sole contribution of the finite inter-
ferogram length to the resolution yields 4.96 cm . The actual FWHM
–1
of the ILS can be written as:
.
FWHM =β 1 207 (10.35)
ILS 2 MPD
where β is a broadening factor to account for parameters other than
the finite interferometer length.
The broadening factor β is mainly due to the finite divergence in
the interferometer, a contribution that varies with the wave number,
being larger for higher wave numbers.
10.8.2 Apodization
As stated in the previous sections, the ILS is governed mainly by the
finite interferogram length and thus closely resembles a Sin(x)/x
function as seen in Fig. 10.11. This function is sometimes considered
a disadvantage because it has amplitude oscillations, which are large
(21 percent for the first ripple), and which die off very slowly. It is
possible to reduce the oscillations of the ILS by using post-acquisition
digital processing on the acquired interferogram prior to Fourier
transformation. This is referred to as apodization, or “removal of feet,”
since the purpose of the operation is to remove or reduce the oscilla-
tions. This improvement of the ILS is gained at the cost of spectral
resolution or increased ILS FWHM. The effect of various types of
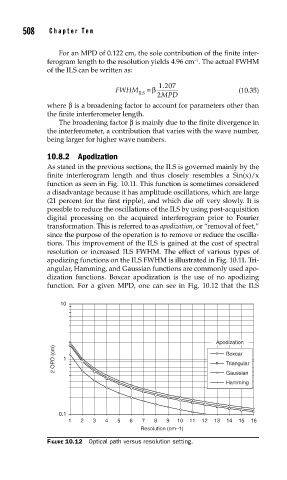
apodizing functions on the ILS FWHM is illustrated in Fig. 10.11. Tri-
angular, Hamming, and Gaussian functions are commonly used apo-
dization functions. Boxcar apodization is the use of no apodizing
function. For a given MPD, one can see in Fig. 10.12 that the ILS
10
Apodization
2 OPD (cm) 1 Boxcar
Triangular
Gaussian
Hamming
0.1
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16
Resolution (cm–1)
FIGURE 10.12 Optical path versus resolution setting.