Page 595 - Sensors and Control Systems in Manufacturing
P. 595
548
Cha p te r
Ele v e n
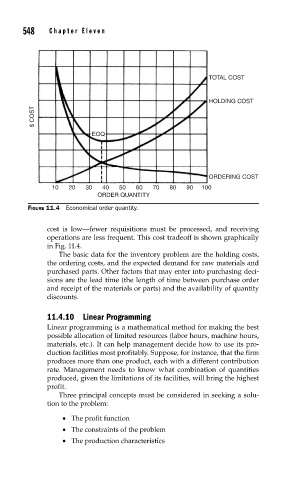
TOTAL COST
HOLDING COST
$ COST
EOQ
ORDERING COST
10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100
ORDER QUANTITY
FIGURE 11.4 Economical order quantity.
cost is low—fewer requisitions must be processed, and receiving
operations are less frequent. This cost tradeoff is shown graphically
in Fig. 11.4.
The basic data for the inventory problem are the holding costs,
the ordering costs, and the expected demand for raw materials and
purchased parts. Other factors that may enter into purchasing deci-
sions are the lead time (the length of time between purchase order
and receipt of the materials or parts) and the availability of quantity
discounts.
11.4.10 Linear Programming
Linear programming is a mathematical method for making the best
possible allocation of limited resources (labor hours, machine hours,
materials, etc.). It can help management decide how to use its pro-
duction facilities most profitably. Suppose, for instance, that the firm
produces more than one product, each with a different contribution
rate. Management needs to know what combination of quantities
produced, given the limitations of its facilities, will bring the highest
profit.
Three principal concepts must be considered in seeking a solu-
tion to the problem:
• The profit function
• The constraints of the problem
• The production characteristics