Page 90 - Sensors and Control Systems in Manufacturing
P. 90
Classification and Types of Sensors
to maintain the desired actual value. Where disturbances occur, the 51
course of the actual value must be continuously observed. When
adjustment is made to continuously regulate the actual value, the
loop of action governing measurement, comparison, adjustment, and
reaction within the process is called a closed loop.
2.3 Understanding Photoelectric Sensors
In order to successfully automate a process, it is necessary to obtain
information about its status. The sensors are the part of the control
system responsible for collecting and preparing process status data
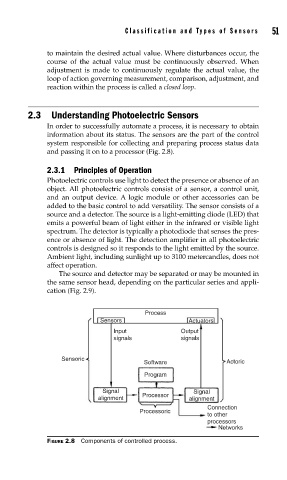
and passing it on to a processor (Fig. 2.8).
2.3.1 Principles of Operation
Photoelectric controls use light to detect the presence or absence of an
object. All photoelectric controls consist of a sensor, a control unit,
and an output device. A logic module or other accessories can be
added to the basic control to add versatility. The sensor consists of a
source and a detector. The source is a light-emitting diode (LED) that
emits a powerful beam of light either in the infrared or visible light
spectrum. The detector is typically a photodiode that senses the pres-
ence or absence of light. The detection amplifier in all photoelectric
controls is designed so it responds to the light emitted by the source.
Ambient light, including sunlight up to 3100 metercandles, does not
affect operation.
The source and detector may be separated or may be mounted in
the same sensor head, depending on the particular series and appli-
cation (Fig. 2.9).
Process
Sensors Actuators
Input Output
signals signals
Sensoric
Software Actoric
Program
Signal Signal
alignment Processor alignment
Connection
Processoric
to other
processors
Networks
FIGURE 2.8 Components of controlled process.