Page 110 - Shale Shakers Drilling Fluid Systems
P. 110
INTRODUCTION 93
the downward stroke, solids do not follow the SHAKER DESCRIPTION
screen. They are, instead, propelled forward along
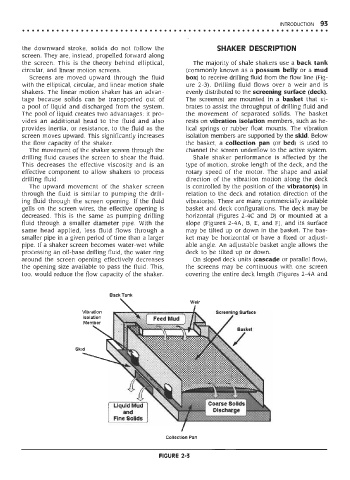
the screen. This is the theory behind elliptical, The majority of shale shakers use a back tank
circular, and linear motion screens. (commonly known as a possum belly or a mud
Screens are moved upward through the fluid box) to receive drilling fluid from the flow line (Fig-
with the elliptical, circular, and linear motion shale ure 2-3). Drilling fluid flows over a weir and is
shakers. The linear motion shaker has an advan- evenly distributed to the screening surface (deck).
tage because solids can be transported out of The screen (s) are mounted in a basket that vi-
a pool of liquid and discharged from the system. brates to assist the throughput of drilling fluid and
The pool of liquid creates two advantages: it pro- the movement of separated solids. The basket
vides an additional head to the fluid and also rests on vibration isolation members, such as he-
provides inertia, or resistance, to the fluid as the lical springs or rubber float mounts. The vibration
screen moves upward. This significantly increases isolation members are supported by the skid. Below
the flow capacity of the shaker. the basket, a collection pan (or bed) is used to
The movement of the shaker screen through the channel the screen underflow to the active system.
drilling fluid causes the screen to shear the fluid. Shale shaker performance is affected by the
This decreases the effective viscosity and is an type of motion, stroke length of the deck, and the
effective component to allow shakers to process rotary speed of the motor. The shape and axial
drilling fluid. direction of the vibration motion along the deck
The upward movement of the shaker screen is controlled by the position of the vibrator(s) in
through the fluid is similar to pumping the drill- relation to the deck and rotation direction of the
ing fluid through the screen opening. If the fluid vibrator(s). There are many commercially available
gells on the screen wires, the effective opening is basket and deck configurations. The deck may be
decreased. This is the same as pumping drilling horizontal (Figures 2-4C and D) or mounted at a
fluid through a smaller diameter pipe. With the slope (Figures 2-4A, B, E, and F), and its surface
same head applied, less fluid flows through a may be tilted up or down in the basket. The bas-
smaller pipe in a given period of time than a larger ket may be horizontal or have a fixed or adjust-
pipe. If a shaker screen becomes water-wet while able angle. An adjustable basket angle allows the
processing an oil-base drilling fluid, the water ring deck to be tilted up or down.
around the screen opening effectively decreases On sloped deck units (cascade or parallel flow),
the opening size available to pass the fluid. This, the screens may be continuous with one screen
too, would reduce the flow capacity of the shaker. covering the entire deck length (Figures 2-4A and
FIGURE 2-3