Page 144 -
P. 144
5.2 Interaction models 127
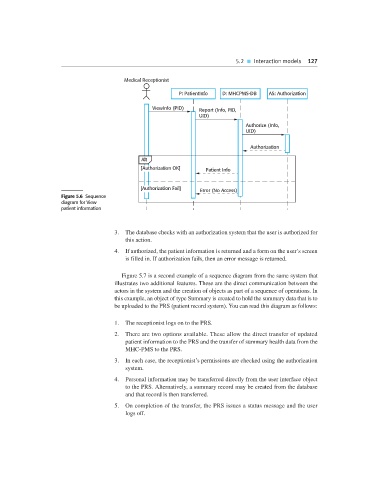
Medical Receptionist
P: PatientInfo D: MHCPMS-DB AS: Authorization
ViewInfo (PID) Report (Info, PID,
UID)
Authorize (Info,
UID)
Authorization
Alt
[Authorization OK] Patient Info
[Authorization Fail]
Error (No Access)
Figure 5.6 Sequence
diagram for View
patient information
3. The database checks with an authorization system that the user is authorized for
this action.
4. If authorized, the patient information is returned and a form on the user’s screen
is filled in. If authorization fails, then an error message is returned.
Figure 5.7 is a second example of a sequence diagram from the same system that
illustrates two additional features. These are the direct communication between the
actors in the system and the creation of objects as part of a sequence of operations. In
this example, an object of type Summary is created to hold the summary data that is to
be uploaded to the PRS (patient record system). You can read this diagram as follows:
1. The receptionist logs on to the PRS.
2. There are two options available. These allow the direct transfer of updated
patient information to the PRS and the transfer of summary health data from the
MHC-PMS to the PRS.
3. In each case, the receptionist’s permissions are checked using the authorization
system.
4. Personal information may be transferred directly from the user interface object
to the PRS. Alternatively, a summary record may be created from the database
and that record is then transferred.
5. On completion of the transfer, the PRS issues a status message and the user
logs off.