Page 147 -
P. 147
130 Chapter 5 System modeling
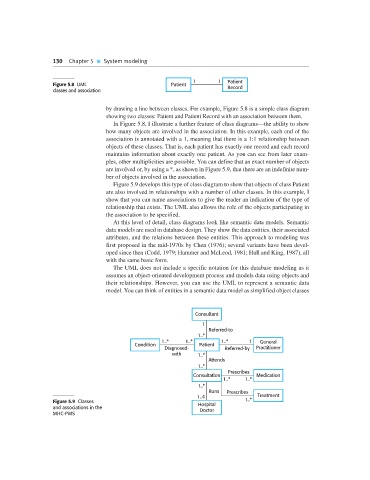
1 1 Patient
Figure 5.8 UML Patient Record
classes and association
by drawing a line between classes. For example, Figure 5.8 is a simple class diagram
showing two classes: Patient and Patient Record with an association between them.
In Figure 5.8, I illustrate a further feature of class diagrams—the ability to show
how many objects are involved in the association. In this example, each end of the
association is annotated with a 1, meaning that there is a 1:1 relationship between
objects of these classes. That is, each patient has exactly one record and each record
maintains information about exactly one patient. As you can see from later exam-
ples, other multiplicities are possible. You can define that an exact number of objects
are involved or, by using a *, as shown in Figure 5.9, that there are an indefinite num-
ber of objects involved in the association.
Figure 5.9 develops this type of class diagram to show that objects of class Patient
are also involved in relationships with a number of other classes. In this example, I
show that you can name associations to give the reader an indication of the type of
relationship that exists. The UML also allows the role of the objects participating in
the association to be specified.
At this level of detail, class diagrams look like semantic data models. Semantic
data models are used in database design. They show the data entities, their associated
attributes, and the relations between these entities. This approach to modeling was
first proposed in the mid-1970s by Chen (1976); several variants have been devel-
oped since then (Codd, 1979; Hammer and McLeod, 1981; Hull and King, 1987), all
with the same basic form.
The UML does not include a specific notation for this database modeling as it
assumes an object-oriented development process and models data using objects and
their relationships. However, you can use the UML to represent a semantic data
model. You can think of entities in a semantic data model as simplified object classes
Consultant
1
Referred-to
1..*
1..* 1..* 1..* 1 General
Condition Patient
Diagnosed- Referred-by Practitioner
with 1..*
Attends
1..*
Prescribes
Consultation Medication
1..* 1..*
1..*
Runs Prescribes
1..4 Treatment
Figure 5.9 Classes Hospital 1..*
and associations in the Doctor
MHC-PMS